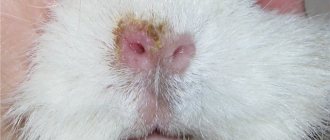
Endoparasites, which include, in particular, worms, are not so easy to detect and eliminate in guinea pigs.
Worms lead a parasitic life in the body of an animal. Undoubtedly, their presence is harmful to animals, since worms absorb nutrients and can cause depletion of the body. All worms, in the course of their life activity, release toxic substances, which causes intoxication of the animal's body.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Feed deficiencies in guinea pigs
Although commercially available pre-mixed foods are usually sufficient for most animals, it is unfortunately common for many guinea pigs to show symptoms of certain nutritional deficiencies. The most common is probably vitamin C deficiency, although it is rarely severe enough to cause obvious symptoms. Therefore, one must constantly be aware of this threat, recognizing that a lack of vitamin C weakens the body's natural immune system and increases the likelihood of disease.
If your pig gets vegetables and fruits, you can be sure that she is not at risk of vitamin C deficiency. In addition to the greens that are usually given, you can slip her a bunch of parsley tops from time to time - they contain a lot of vitamin C. Almost all guinea pigs eat her very willingly.
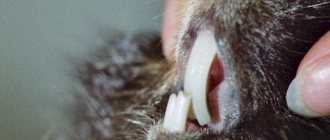
Progressive deficiency of vitamin C leads, as in humans, to scurvy. Here is what the famous German writer and journalist Bernhard Grzimek writes about this in his book “Our Little Brothers”: “... these funny fat animals have one thing in common with us humans: they can, like us, get scurvy. True, in their homeland, Peru, where a lot of both wild and domestic guinea pigs roam, they have never suffered from such a disease. It is we, people, who awarded the unfortunate experimental animals with such a disease.” In the process of evolution, they have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C. Symptoms of scurvy are loose teeth, and in an extremely acute form - attacks, during which the animal usually lies on its side with outstretched paws and an expression of pain on the face. In this case, the only salvation can be a strong dose of vitamin C, preferably in the form of a solution, which is given according to the instructions of a veterinarian.
Guinea pigs can be given at least 5 mg of vitamin C daily in their drinking water. As an approximate dose, we can recommend 1 mg of ascorbic acid per 1 ml of water. Since ascorbic acid easily enters into chemical reactions, the solution must be changed daily. When keeping a guinea pig at home, it needs an average of 20 mg of vitamin C per day.
In cases of other vitamin deficiencies, for example, those manifested by hair loss or skin allergies, it is recommended to give a multivitamin preparation daily. In addition, of course, one should strive to exclude the cause of the disease, because with proper nutrition such a problem should not arise in principle.
Already weakened animals catch cold easily. This occurs mainly when food shortages are accompanied by incorrect placement of the cage. When your pig catches a cold, it is necessary to: eliminate the root cause of the disease; keep the animal warm; try to strengthen his immune system by increasing the dose of vitamins.
Less dangerous, but also unpleasant, are eye inflammations caused by drafts. In this case, the first step should also be to move the animal from an unsuitable place. In addition, eye drops prescribed by a veterinarian are used.
In order not to expose your guinea pig to the danger associated with sudden changes in temperature, you can take it out onto the balcony only when the weather is really warm. This South American rodent feels best at temperatures around 20°C. Animals kept outside the home should regularly receive vitamin C in preventive doses.
Ectoparasites
Skin parasites in guinea pigs belong to the group of ectoparasites. The most common among them are lice and ticks, as well as lice and fleas. The first symptom of infection with any of the skin parasites is severe itching, redness and baldness of the infected areas of the skin.
Skin parasites cause various diseases, most of which lead to exhaustion of the animal, the appearance of numerous purulent ulcers on the body and even death. Death occurs not only in case of exhaustion, but also as a result of blood poisoning. Various viruses and pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the blood through open wounds and ulcers.
Fleas
Cat fleas are most common in guinea pigs. They can get on the animal from another animal, from the street, and a person can also become a carrier of fleas. Symptoms of the appearance of parasites are itching, local hair loss, and the presence of scratched wounds. If there are too many fleas, this can lead to anemia, exhaustion, and blood poisoning. Detecting fleas is not difficult - you can use a regular fine-tooth comb for fur.
The pig needs to be combed well and checked to see if any insects are stuck between the teeth of the comb.
Treatment of fleas is not complicated, but it requires attention and treatment of not only the sick animal, but also all other pigs. The animal should be treated with any shampoo or spray containing pyrethritol. The entire cage should be washed with the same shampoo, the bedding should be changed and the entire area around the cage should be treated. The procedure should be repeated after ten days and, if necessary, after another ten days. Usually two procedures are enough to destroy not only insects, but also their larvae.
Ticks
Guinea pigs are most often parasitized by two types of mites: the scabies mite and the fur mite.
Scabies mite
The subcutaneous mite in a guinea pig can cause very severe itching. An animal infected with scabies mites can not only injure itself, but also die from severe stress and exhaustion. Symptoms of subcutaneous scabies mite infestation:
- Itching,
- Excessive hair loss
- Skin redness,
- Dry skin
- Increased body temperature
- Refusal of food
- The appearance of papules, ulcers, and wounds on the skin.
Most often, ticks settle in the skin of the head, back, sides and shoulders, but with severe infection they quickly spread throughout the body. Open wounds become a source of penetration of dangerous bacteria and infections into the blood, which increases the risk of secondary infection. If a pregnant female is infected with mites, there is a high risk of miscarriage and subsequent complications.
A guinea pig can become infected with ticks from other animals, as well as from humans - insects can live on clothing and even on a person’s body without causing him any discomfort. The presence of a tick in the skin of an animal can only be determined by scraping. Not only the infected guinea pig is treated, but also everyone in contact with it. Usually a ten-day course of ivarmectin injections is sufficient.
Along with the injections, the cage should be thoroughly washed with a solution of lime sulphide or a strong chlorine-containing solution.
Viruses and bacteria in guinea pigs
Diseases caused by bacteria and viruses are very difficult to recognize for an inexperienced person, and in most cases, the intervention of a veterinarian is necessary to save the animal.
The most dangerous viral diseases, without a doubt, are “guinea pig pestilence” and “guinea pig paralysis.” Both have almost identical symptoms - seizures and paralysis, particularly in the hind limbs. There are also many other viral diseases that are not so common, but just as dangerous. Symptoms such as shaggy, matted fur, nasal discharge, coughing, diarrhea and noticeable changes in behavior may be signs of a viral illness.
The fundamental principle of action in the presence of any viral disease is the immediate isolation of the infected animal from the rest. For there is a great danger of the spread of pestilence.
Symptoms: exudate (effusion) from the nose, purulent eyes and eyelids, disheveled fur, diarrhea, weight loss, paralysis, vomiting, heavy breathing, convulsions, obvious changes in behavior.
The most common bacterial disease in guinea pigs is pseudotuberculosis. Its outward symptom is diarrhea, leading to exhaustion and ultimately paralysis. This disease is also highly contagious and can kill an entire brood within days or weeks.
A runny nose, which can quickly turn into pneumonia, is also dangerous. The mortality rate among sick guinea pigs in this case reaches 50%.
So, as you can see, the variety of external (clinical) symptoms of infectious diseases is quite large. In addition, the same symptoms can accompany different diseases. Actions in each individual case should be determined by a veterinarian.
Treatment
Worms are removed from guinea pigs, usually with medications for cats and dogs. Since a wide range of medications specifically for rodents are not produced. It is better when a veterinarian prescribes medications and determines their dosage.
Known treatments:
- suspension for deworming rodents “Shustrik”,
- "Dirofen paste" for puppies,
- suspension "Prasicide" for kittens.
They should be used strictly according to the instructions; the dosage can be calculated based on the pet’s body weight. For treatment use any one remedy. These drugs are not used for prevention.
Worms in guinea pigs require immediate treatment! And in the case of using modern drugs, treatment will give a fairly quick positive effect.
To reduce the risk of infecting the animal with worms, the pig’s cage and objects for use should be cleaned on time, especially the toilet. Feed with professional food, give fruits and vegetables only washed, and drink filtered water. If the guinea pig is completely domestic and does not come into contact with the street or other domestic animals, but has become infected with worms, then the source is in the apartment. In this case, you need to do a general cleaning - parasite eggs could be brought into the apartment with any outdoor item.
Did you like the article? Share with friends: [supsystic-social-sharing id=”1"]
- Related Posts
- American Teddy Guinea Pig
- Subcutaneous and ear mites in guinea pigs, symptoms and treatment
- Guinea pig breeding
« Previous entry
Parasites in Guinea Pigs
Parasites are divided into two groups. The first consists of internal parasites (endoparasites), which destroy the internal organs of the host body. Another group are external parasites (ectoparasites), which live in the fur or cling to the skin of the animal.
Endoparasites, which include worms in particular, are not so easy to identify and eliminate. Tapeworms (tapeworms), worms and liver flukes are the most common internal parasites of guinea pigs. Their presence can be manifested in weight loss and changes in the appearance of the animal's feces. A healthy pig's stool is dry and oval in shape. Depending on the food consumed, their color varies - from brown to green and even orange (after eating carrots). However, the presence of certain parasites can only be detected by a veterinarian based on a special blood or stool test. In general, we can say that the danger of invasion by internal parasites is negligible if the cage is kept clean and the quality of the food given to the pig is impeccable.
Ectoparasites include fleas, lice eaters, ticks, and guinea pigs bred outside also have blood-sucking mites. Animals affected by these parasites often itch, shake, and exhibit restless behavior. Noticeable skin manifestations include bald, red, flaky or scabby areas. At a more advanced stage of parasite infection, allergic eczema and festering wounds appear, which are easily susceptible to bacterial infection.
Ectoparasites are killed by various commercially available aerosols. In the event of a massive appearance of parasites, affected pigs should be sprayed with the drug daily or every other day, carefully ensuring that the poison does not get into the eyes, nose or face of the animal. Preparations in the form of powders are also recommended, the use of which is more pleasant for the animal, since it does not disturb it with a strong stream, as happens when using aerosols.
Trixacarosis
The causative agent of the disease is the microscopic scabies mite Trixacarus caviae, which parasitizes the subcutaneous layer. It differs in that it affects only guinea pigs, so infection occurs exclusively through sick relatives.
This disease is especially difficult for young and elderly individuals, animals exhausted by other diseases, pregnant females and pigs that are kept in inappropriate conditions. Suspicion of trixcarosis arises from the following signs:
- severe itching and soreness of the affected areas of the skin;
- the animal scratches the skin with its claws and teeth;
- hair loss and the appearance of significant areas of baldness;
- open ulcers and wounds on the skin;
- lethargy of the animal, refusal of food and drink;
- cramps.
If the disease is advanced, the female may have a miscarriage. If animals are not treated at all, they die.
Trixacarosis is diagnosed by skin scraping in a veterinary clinic, and the animal is treated there.
As treatment, injections are prescribed with one of the antiparasitic drugs: otodectin, ivermectin, ivermec or novomec.
Wounds in guinea pigs
The hair around the wound should be cut off, the wound should be cleaned of dirt and hair and washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate 1:1000; then lubricate with Vishnevsky ointment or any other disinfectant ointment (streptocidal, syntomycin, prednisolone). The wound is treated daily. On the 3-4th day, the wound can be sprinkled with streptocide or a complex powder (xeroform, streptocide and boric acid in equal parts). After treatment, it is recommended to apply a light bandage.
Fractures and cracks of bones in guinea pigs
For bone fractures, the obligatory signs are swelling, severe pain, increased local temperature, and lameness. With an open fracture, soft tissue is damaged.
Treatment: for an open fracture, first treat the wound and then apply a plaster cast or splints. For open fractures, a bandage is applied so that the wound remains open for daily treatment. The plaster cast is removed after 3 weeks, and if fusion has not occurred, the bandage is applied again.
Conjunctivitis in guinea pigs
Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye). The causes of this disease are mechanical damage. Unilateral conjunctivitis affects one eye, bilateral conjunctivitis affects both eyes.
Signs of the disease: redness and swelling of the eyes, squinting and sticking together of the eyelids, photophobia, lacrimation. This initial catarrhal form of conjunctivitis can turn into a purulent form, in which purulent discharge from the eyes is observed, the eyelids stick together, and the skin around the eyes becomes inflamed. In advanced cases, clouding of the cornea begins and vision loss occurs.
Call a veterinarian to your home
Treatment: dry purulent crusts are soaked in a 3% solution of albucid and then carefully removed using tweezers and a cotton swab. Then an eye ointment - hydrocortisone or tetracycline - is placed under the eyelids. The same ointment is also applied around the eyes. When the cornea is clouded, good results are achieved by blowing calomel and powdered sugar into the eyes, mixed in equal parts; Insufflation is performed daily 2 times a day until cure. In the initial stage of the disease, 4-6 injections are usually sufficient.
Routes of infection and stages of treatment
The main reason helminths enter the body is food. Products become contaminated when sanitary standards are violated in production. Or due to improper storage, when the product is not isolated from sources of contamination. It is better to wash vegetables and fruits before offering them to your pig. Worms can be found in dirty tap water. Therefore, animals are given only filtered or boiled water.
Another possible option is that the infection occurred on the street, if the pet is taken out there for a walk. The animal eats something dangerous or parasites fall on it from plants or the ground. If the pig is not allowed outside the house, parasites can appear along with any item that has been outside: shoes, clothes. In addition, worms easily pass from one living creature to another if personal hygiene standards are not observed.
Helminths are removed with special drugs that are sold in a veterinary pharmacy. But first it is better to show the animal to a veterinarian. Perhaps the parasites have caused serious harm to the pet and he will need additional medications.
Rickets in guinea pigs
This is a disease of the body that occurs as a result of the lack or absence of mineral salts and vitamin D in feed, as well as from disruption of the activity of the endocrine glands. As a rule, rickets most often occurs in young animals, especially in winter with a lack of sunlight.
Signs of rickets: thickening of joints, curvature of limbs, sagging back, stunted growth.
Treatment: the sick animal is placed in a clean, bright room; Give 1-2 drops of trivitamin or tri-vitamin orally per day. Irradiation with a quartz lamp for 10-15 minutes for 10-15 days is very useful.
What symptoms indicate the presence of fleas
Signs that an animal is being bitten by fleas are as follows:
- redness and peeling of the skin, bite marks (usually on the stomach) in the form of red dots;
- the pig behaves restlessly, shakes its head, itches, eats poorly, becomes less active;
- In places where insects accumulate, hair loss may occur.
Insects pierce the skin and drink blood. The bites are painful, and there are no anesthetics in the saliva. In the affected areas, the skin becomes inflamed, itches, and hurts when scratched.
Flea bites cause red spots on your pig's skin.
Digestive diseases in guinea pigs
Diseases of the digestive system occur as a result of improper feeding or prolonged hypothermia, as well as due to infection.
Signs of the disease: loss of appetite, diarrhea, general depression, limited movement.
Treatment: first of all, you need to cleanse the animal’s gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, give a tablespoon of vaseline or castor oil orally, and then biomycin, syntomycin, levomycin, phthalazole or enterosep-tol, 1/3 tablet 2 times a day; as a drink - a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate or strong tea; for constipation - Vaseline or castor oil.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of ringworm appear 4-6 weeks after the patient becomes infected. A red spot appears on a smooth area of skin of a child or adult. It rises above the surface and has smooth boundaries. Over time, the size of the lesion increases. The surface becomes covered with nodules, blisters and scabs. The spots develop into rings that can intersect or merge with each other. The diameter of skin formations ranges from 5 to 30 millimeters.
Signs of ringworm include an acute inflammatory reaction. It often develops in children and girls. The lesions begin to peel off intensively. Patients suffering from dermatitis do not immediately identify symptoms of microsporia. Areas of active fungal growth may appear as inflammatory skin lesions.
A common manifestation of ringworm in a child is damage to the scalp. This symptom affects patients aged 5-12 years. Older children experience changes in the chemical composition of sebum. Its elements become dangerous for the microsporia pathogen.
The suppurative type of ringworm is characterized by the appearance of soft nodules on the patient’s skin. The nodes are dotted with numerous abscesses. When they are compressed, purulent contents are released.
Are you experiencing symptoms of ringworm?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Respiratory diseases in guinea pigs
Respiratory diseases - inflammation of the upper respiratory tract and lungs - occur when the body is overcooled or exposed to a draft.
Signs of the disease: general weakness, increased body temperature, rapid difficulty breathing, increased thirst and decreased appetite; animals lie down more and react weakly to nicknames and external irritations.
Treatment: first of all, you need to create good living conditions for the animal; Sulfonamide drugs are used for therapeutic purposes.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis and treatment of ringworm are carried out by a dermatologist. The doctor examines the patient and identifies typical manifestations of microsporia. Examination of skin scrapings under a microscope reveals fungal mycelium and changes in the structure of hair and skin. Differential diagnosis makes it possible to exclude trichophytosis from the patient’s history, which has similar manifestations upon microscopy of the patient’s biomaterials.
Microflora culture appears to be a more informative diagnostic technique. Laboratory staff determine the type and genus of fungi. Based on the laboratory report, the dermatologist selects drugs that will cure the patient.
Luminescent examination makes it possible to identify pathological lesions on the skin of the patient and those living with him. This diagnostic method is based on the green glow of the fungal mycelium under the influence of a gas-discharge light source.
Pasteurellosis in guinea pigs
The causative agent of the disease is a microbe. It is not stable in the external environment and can be quickly destroyed with disinfectants.
A characteristic sign of the disease is a runny nose. At first, only moistening of the hairs around the nostrils is noted, then sneezing, the animal rubs its nose with its front paws. A mucous and then purulent discharge appears from the nasal cavity. Breathing is heavy, with wheezing. The disease can last for several months, either subsiding or worsening. There are complications in the form of ulcers on various parts of the body. When the causative agent of this disease enters the bloodstream, blood poisoning occurs, accompanied by high fever, general weakness, diarrhea, and sometimes convulsions. There is no specific treatment for the disease. Sick animals with obvious clinical signs should be destroyed. If a disease is suspected, animals are given symptomatic treatment by giving oral antibiotics (50-100 thousand action units per day) and sulfonamide drugs (1 tablet per day) as prescribed by a veterinarian.
Prevention
If in addition to the guinea pig, there are other pets in the house - cats or dogs, they must be regularly treated with insecticides so that they do not catch the infection and “reward” the little pet with it. This rule especially applies to those pets who are allowed to go outside for a walk.
The usual requirements for the conditions of keeping a pig play the role of preventive measures. These include:
- cleaning the animal's house;
- changing filler and bedding;
- treating the pet's cage and items with disinfectants.
All this should be done regularly and on an ongoing basis, and not just during or after an illness. Before going on walks, your pig needs to be protected against parasites.
It is very important to seek medical help at the first symptoms of infection. The consequences of an advanced disease are irreversible for the animal’s body, which leads to its death. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chances of ridding your pet of the disease and returning him to his normal life and normal well-being.
It is not worth treating the animal on your own - only a veterinarian can prescribe the correct treatment. Self-selected therapy can cost the animal its life. Control by a veterinarian and a responsible approach to healing your pet are the key conditions that will soon allow you to see your pet healthy and active.
Worms in guinea pigs
Worms lead a parasitic life in the body of an animal. Undoubtedly, their presence is harmful to animals, since worms absorb nutrients and can cause depletion of the body. All worms, in the course of their life activity, release toxic substances, which causes intoxication of the animal's body. Worms are flat (tape) and round.
Tapeworms live in the intestines and look like a narrow ribbon consisting of individual segments and tapering to one end, on which is a head with suckers. The further the segment is from the head, the more mature it is. When the testicles mature in it, it breaks off and is released with feces into the external environment. Embryos emerge from the testicles of a segment that is eaten by an animal. They pierce the intestinal wall, enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. A cyst can form in various internal organs or in the brain of an animal, where the embryos of worms are located, which are very dangerous for humans.
Roundworms come in many types. Some of them look like thin threads of whitish and pinkish color; they often live in the intestines, sometimes in the liver and lungs. When animals defecate, mature testicles are released into the external environment. Infection occurs when animals eat them in food; Upon contact with such animals, humans can also become infected.
If any worms are detected, you must contact a veterinarian who will prescribe treatment.
For ascariasis, a good result is achieved by using piperazine (as prescribed by a doctor). Personal hygiene must be strictly observed.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Worms in fish: are there river or sea fish? Is it possible to eat raw or salted fish with worms?
Fish parasites: helminths parasitizing sea and river fish
Subcutaneous worms in humans, cats and dogs: what are the symptoms and treatment methods
What do worm larvae look like: round and tapeworms, flukes
No to ticks: where to order insect repellent treatment?
Do chickens have worms: first signs and medications for treatment