Hamsters are one of the most popular pets. And this is not surprising - they are small, undemanding to care, and easy to maintain. Those who are just planning to get such a pet should find out how a hamster lives, everything about the varieties of rodents, their lifestyle, nutrition and reproduction. This information will help organize suitable living conditions for the animal and avoid mistakes in care that can be fatal.
Description of the rodent
Red hamster eats a leaf
– Advertisement –
Hamsters are small rodents with a dense build, short legs, small ears and short tails. The body length ranges from 5 to 34 cm, the tail is from 0.7 to 10 cm in length. Females can exceed males in size. The fur is thick, the back is colored from ash or brownish-gray to dark brown-ochre. The abdomen is found in black, white or gray. There is a pronounced black stripe on the back. Hamsters also differ from other types of rodents in having well-developed cheek pouches.
Syrian breed of hamsters
Owners should think in advance about how much a Syrian hamster weighs, since it is much larger than a dwarf hamster.
An adult furry pet can reach a size of about 19 cm and is a fairly large representative of its family. The animal loves to communicate with people and is willing to be held.
Such a pet weighs 100-200 grams. It is typical for this breed to have both long and short hair. Best for a hamster:
- Housing size 40*60 cm.
- Treadmill with a diameter of 18 cm.
- Living without neighbors.
Article on the topic: Why does a hamster lose hair and peel off its skin: is it shedding or is it sick?
Hamster nutritional features
A hamster eats corn at a small table.
Hamsters are omnivorous rodents, but their diet is dominated by plant foods. In addition, hamsters feed on insects and their larvae, small vertebrates (mice, reptiles and amphibians). In the autumn, they switch to seeds and tubers, and also store them in quantities from 0.5 to 11-16 kg. Sometimes hamsters' storerooms with grains and potatoes reach 90 kg. Hamsters also bring grain, peas, rice, millet, buckwheat, lupine, corn, lentils, potatoes to the pantries, putting different varieties of seeds separately. The hamster feeds on these reserves in the winter, temporarily waking up from hibernation, and in the spring until fresh food becomes available.
The hamster carries food in its cheek pouches, which contain about 46 g of wheat. Can carry food for about 1 km.
Record holders for size
The largest hamster in the world is the capybara Caplin Rose. The owner of the giant pet is Melanie Typaldos. The weight of the animal is 64 kg, and the body length is 1.4 meters. Melanie named her pet after the huge rodent from the fairy tale “The Princess Bride.” Typaldos claims that the animal is very friendly and plays with children and even dogs.
A hamster's favorite pastime is to swim in the river, and then eat ice cream and fall asleep. Melanie even writes a blog about her pet, which is popular.
Hamster spread
— Advertising —
Hamster distribution map
Hamsters are widespread in Central and Eastern Europe, Asia Minor, Syria, Iran, Siberia, Mongolia, northern China and Korea.
The largest populations live in the forest-steppe and steppe. In the south it prefers damp areas, such as river valleys. In the mountains it is found at altitudes up to 3600 m above sea level, up to mountain meadows and forests. It also develops cultivated areas, such as rice fields, forest belts, parks, orchards, vegetable gardens, and residential buildings. Prefers dense soils, rare on sandy soils.
Conservation status
Until 1960, the soft-haired animal was the object of the fur trade in Czechoslovakia, Germany and the USSR. A sharp decline in numbers forced the cessation of fur harvesting in the middle of the 20th century. Western European countries have approved national programs to ensure the conservation of this species.
These include Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, France, Belarus and Ukraine. It is also protected in five constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The number of animals is unchanged in Siberia and Kazakhstan, and the number of animals in the Krasnodar Territory and Azov District of the Rostov Region causes significant damage to agriculture. Although the total number of the species continues to decrease.
Did you know? Smart hamsters can remember their name and perform some tricks.
Common types of hamster
Common hamster (Cricetus cricetus)
A common hamster emerges from its burrow.
The body length of adult males is 27-34 cm, the tail is 3-8 cm long, weight is about 700 g. The tail becomes thinner towards the end, covered with short, stiff hairs. The ears are short and dark. The fur is thick and soft. The color is bright and contrasting. The back is reddish-brown, the belly is black. On the sides there are two large light spots separated by black fur. There are also light spots on the sides of the head and behind the ears. There are specimens that are black or black with white spots on the legs and neck. In total, more than 10 subspecies of the common hamster have been described. The color becomes lighter from north to south, body size increases from west to east and from north to south.
The species lives in the meadow and forest-steppe of Eurasia from Belgium to Altai and Northern Xinjiang.
Syrian hamster, or Central Asian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus)
Syrian hamster in its burrow
Body length is about 13 cm, tail up to 1.5 cm. Weight ranges from 100 to 125 g. The fur is soft, thick, golden.
It is found in nature near the Syrian city of Aleppo and in eastern Turkey.
Brandt's hamster or Transcaucasian hamster (Mesocricetus brandti)
The Caucasian hamster hides in the grass.
Body length is 15-18 cm, tail length is 2-3 cm. Weight is up to 300 g. Ears are small. The back is earthy brown. The belly is brownish-gray, there is a black spot on the chest. The sides of the head are yellowish-red, there are long black spots under the ears, and the chin is white. Paws are white. The fur is soft and thick on the tail.
The species' habitat includes Turkey, Israel, Lebanon, and the eastern Ciscaucasia. Inhabits steppes on mountain slopes, mountain meadows and cultivated areas.
Radde's hamster or Cis-Caucasian hamster (Mesocricetus raddei)
Radde's hamster in the grass - photo
Body length up to 28 cm, tail length about 1.5 cm. The back is brownish. The belly is black or dark gray. There are light spots on the cheeks and behind the ears.
Distributed in Georgia and Russia, in the North Caucasus, in the Stavropol Territory and in the Ciscaucasia, in the steppes and forest belts.
Newton's hamster (Mesocricetus newtoni)
Newton's hamster in the steppe
Body length 14-17 cm, tail length up to 2 cm, weight 80-150 g. The back is gray-brown, with a black stripe running down the center of the back. The neck and chest are black-brown, the belly is yellowish-gray.
Found along the Danube, in Bulgaria and Romania.
Djungarian hamster (Phodopus sungorus)
Djungarian hamster
Body length up to 10 cm, weight 35-65 g. Gray back decorated with a dark stripe, short tail. Fur with white spots.
Inhabits dry steppes and semi-deserts in the south of Western Siberia, Dzungarian Alatau, and Khakassia.
Campbell's hamster - photo
(Phodopus campbelli)
Body length is 7-10 cm, the tail is short, up to 1.5 cm long, weight is about 25 g. The head is rounded, the muzzle is short. The fur is dark gray with a brown tint, there is a dark stripe on the back, and the belly is gray.
The species is distributed in Mongolia, northern China, Russia and Kazakhstan.
Roborovski's hamster (Phodopus roborovskii)
Roborovsky hamster photo at home
A small species with a body length of 4-5 cm, weighing about 30 g. The head and back are sandy-golden, the abdomen is white. Light spots are visible above the eyes.
Found in Mongolia, China and Russia.
Short-tailed hamster (Cricetulus alticola)
Short-tailed hamster in the grass
Body length is 8-10 cm, weight ranges from 22 to 48 g. The fur is gray-yellow-brown without spots.
It lives in the north of South Asia and China, at altitudes of about 4000 m above sea level, in coniferous and birch forests, and in the steppes.
Barabinsky hamster (Cricetulus barabensis)
Barabinsky hamster - photo
Outwardly similar to an ordinary hamster. Inhabits forest-steppe and semi-deserts in the south of Western Siberia, Tuva, Transbaikalia, Mongolia, northeast China, Primorye (Russia) and Korea.
Gray hamster (Cricetulus migratorius)
Gray hamster in the steppe - photo
Body length 10-13 cm, tail 2-3.5 cm long. The coat is gray on top, the abdomen and tail are light. The eyes are large. The ears are small.
The species' habitat includes Eastern Europe, Russia, Asia to western China.
Sokolov's hamster (Cricetulus sokolovi)
Sokolov's hamster on a stone
Body length from 7 to 11 cm, tail length up to 3 cm. The back is gray with a dark stripe. The abdomen is light gray. There are dark brown spots in the center of the ears.
Found in sandy areas of Mongolia and China.
Mongolian hamster (Allocricetulus curtatus)
Mongolian hamster in the Berlin Zoo
A small species with a body length of 10-15 cm, a tail 1.5-2 cm long. The color is light, the tummy, tail and paws are white. The tail is fluffy.
It lives in the Zaisan depression in the south of Tuva, China and Mongolia.
Eversman's hamster (Allocricetulus eversmanni)
Eversman's hamster - photo
Body length 13-16 cm, tail 2-3 cm long. Legs short. The ears are small. The tail is wide, flattened, densely pubescent. The fur is short, soft, velvety. The back is blackish-brown or fawn-red or ash-sandy. The belly is white with a sharp border on the sides. There is a brown spot on the throat and chest. The paws and tail are white below.
Lives in the Lower and Middle Trans-Volga region, in the south of the Trans-Urals, in Kazakhstan.
Kansky hamster (Cansumys canus)
The Kansky hamster lies on its stomach.
Body length is from 10 to 17 cm, tail is 7-10 cm. Weight is from 60 to 120 g. The fur is thick, the back is gray with white spots on the cheeks and near the ears. The belly and tip of the tail are white.
The species is distributed in central China.
Rat-like hamster (Tscherskia triton)
Body length from 14 to 25 cm, tail 7-10 cm long. Weight from 92 to 241 g. The back is light gray-brown, the tail is dark brown with a white tip, the paws are white.
The habitat includes northeast China, the south of Primorsky Krai, and Korea.
Body structure
Hamsters look harmonious and proportional.
The structure of their body is characterized by the following features:
| Body type | Dense, knocked down |
| Body length (excluding tail) | 5–35 cm |
| Weight | 30–700 grams |
| Head | Not very large, round, on the muzzle there are hard whiskers (“whiskers”) of a dark color. |
| Ears | Small, rounded, on the outside the ears are covered with dark hairs, finer than the main fur. |
| Eyes | Little ones |
| Tail | Short, no more than 10 mm. It is thick at the base, then sharply tapers into a triangle shape. May be bare or covered with coarse and short hairs |
| Paws | Small but strong, with wide hands and feet. The toes have hard and strong claws, with the help of which the animal is able to dig holes even in very dense soils. Some species have bare limbs, others are covered with hair (this group is called “hair-footed”) |
| Wool | Thick and soft |
| Teeth | Sharp, strong. Teeth have no roots, but they grow throughout the rodent’s life. |
A distinctive feature of hamsters is the presence of special muscle cavities located in the lateral parts from the inner surface of the cheeks to the neck and very shoulders. These are the so-called cheek (or cheek) bags. For the rodent, they act as a kind of container into which the animal loads large supplies of food and then transfers them to the hole, where a stationary storage facility has already been installed, allowing the animal to be provided with food throughout the winter.
The presence of cheek pouches can make a hamster's life much easier. In addition to carrying food, the animal can use this feature of its physique for more original purposes, for example, swimming. The animal fills the volumetric cavity in the upper part of its body with air and thus receives an excellent “life preserver.”
Did you know? Cheek pouches are found not only in hamsters, but also in other rodents, including ground squirrels, chipmunks, harelips, pouched rats, and gophers. It is interesting that many species of monkeys have the same formations, but vultures, wolves and coyotes in the process of evolution have learned to use a safer place to transport food - their own stomach.
Hamster behavior
Hamster on a walk
Hamsters are terrestrial animals; some species can swim by taking air into their cheek pouches. They usually live alone, in burrows. Outside the breeding season, hamsters behave aggressively towards their relatives and often start fights. In winter, they fall into a prolonged torpor, which is still not real hibernation.
Hamsters are characterized by a twilight lifestyle. During the day they remain in their burrows, which reach 8 m in length and 1.5 m in depth. May occupy gopher burrows. In a permanent burrow there are from 2-5, sometimes up to 10 exits, a nesting chamber and storerooms.
Karbysh lifestyle
Like other rodents, carbysh prefers to lead a nocturnal lifestyle. During the day it hides in a hole, and in the evening it comes out to inspect the property and replenish supplies. The “storage room” of a field hamster is designed for a comfortable existence for several months.
Hamster burrows are 5–10-meter labyrinths with separate compartments for storing supplies, resting and sleeping, and even a toilet. Karbysh prefers to use ready-made tunnels that have already been dug by gophers or other rodents. The hamster can easily drive them out, but more often he picks up abandoned holes, which he then skillfully modernizes. The animal's burrows are clean. The animal is an example of a zealous owner.
During the warm season, he is actively engaged in replenishing supplies, expanding the territory, and taking care of procreation. A slow metabolism allows him to sleep in winter.
In Russia, field hamsters are common in the Caucasus, Altai and Siberia. The habitat of the animal includes Kazakhstan and China, many European countries.
Hamster breeding
A female hamster with her offspring
Hamsters are known for their fertility, producing 2-4 litters per year. The duration of pregnancy is from 15 to 22 days, in one litter there are from 1 to 18 babies, they become sexually mature already at the 6-8th week of life. Under natural conditions, hamsters live from 1 to 3 years, at home about 3 years.
Survival Secrets
Field hamsters have a hard life. Dangers lie in wait for them everywhere, at any time of the year. No matter how the carbysh hides, it can become prey for foxes, martens, birds of prey, especially kites. In the wild, the animal lives 2–3 years; if kept at home, its eyelids can be doubled.
The field hamster is considered an aggressive animal, but upon closer study of its habits it becomes clear that, just like Wolverine, it will never attack first. When a karbysh is threatened, he takes a militant pose and tries to make it clear with all his appearance: “Don’t touch me, when I’m angry, I’m very dangerous!” He drives away the uninvited guest until the last moment, and begins to bite when he has no choice. The bites are very painful; for many animals, an encounter with a rodent ends in failure.
The defensive aggression of the field hamster is forced; the animal cannot be condemned for this. This is his principle of survival.
Natural enemies of the hamster
The main enemy of the hamster is the heron.
Hamsters become victims of such predators as the red and black kite, buzzard, lesser spotted eagle, fox, ermine and badger. Kestrels, gray herons, carrion crows, and rooks prey on the young.
Notes
- Sokolov V. E.
Five-language dictionary of animal names. Mammals. Latin, Russian, English, German, French. / under the general editorship of academician. V. E. Sokolova. - M.: Rus. lang., 1984. - P. 156. - 10,000 copies. - [genomics.senescence.info/species/entry.php?species=Cricetus_cricetus Black-bellied hamster (Cricetus cricetus) longevity, aging, and life history]. Retrieved January 3, 2013. [www.webcitation.org/6Do9jpKM0 Archived from the original on January 20, 2013].
Pet hamsters
Domestic hamster in a cage
Syrian, Djungarian, Campbell and Roborovian hamsters are kept at home. Syrian hamsters come in a wide variety of colors, patterns, and coat types. Long-haired Syrian males are sometimes mistakenly called "Angora".
When choosing a hamster, take into account that Roborovsky hamsters can live in flocks, while other species are solitary, and when they are kept together, fights arise, which often lead to the death of the weaker of the hamsters. When hamsters of different sexes are kept together, the female gives birth very often, which harms her health and shortens her life. A pregnant female is capable of killing or injuring a male while protecting her cubs.
The dimensions of the cage for hamsters must be at least 50 cm by 30 cm. A wheel with a running surface (14-18 cm in diameter) must be installed in the cage. Eating at home is no different from eating in nature. The diet is based on cereals and green plants.
For mating, a pair is selected from a male aged 4 months and a female aged from 9 months. They are brought together on neutral territory or in a male’s cage during the female’s estrus period, which occurs for several hours every 4 days. Pregnancy lasts from 17 to 20 days. At the age of 4 weeks, the young animals are separated from the female, separated by gender.
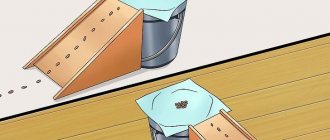
How to weigh a hamster?
A hamster is a nimble animal that is difficult to keep in one place for a long time. If the pet is disobedient and untamed, you will have to cheat to find out the weight of the hamster. Use these short instructions to help you quickly measure your khoma without causing discomfort.
- Get your electronic scales ready. A regular kitchen scale will do. Their accuracy should be sufficient to weigh a light hamster.
- Take a container that matches the size of the animal. Without such an “accessory,” the animal can easily escape and it will not be possible to measure its “parameters.” The container will help contain the animal for at least a few minutes. You can use a regular glass or bowl. Before weighing, the tare weight should be reset to zero.
- To help your pet sit still, place a couple of sunflower seeds or another light treat in the container. This will interest the animal, and it will be calm for a while.
After you manage to measure the khoma, the result needs to be written down. This will help control weight loss or gain. Rapid weight loss indicates the presence of diseases. Weight control is also helpful when changing your diet or diet. This will ensure that your pet is eating new food and not hiding it in corners. A healthy hamster should weigh as much as is normal for an animal of its breed and age.
Article on the topic: How to determine the sex of a red-eared turtle: distinguishing boys from girls
Interesting facts about the rodent:
- The word “hamster” is of Old Church Slavonic origin, in turn borrowed from ancient Iranian, where “hamaēstar” is translated as “an enemy who throws to the ground.” This probably indicated that the hamster bends the stem of the cereal towards the ground and thus gets the seeds.
- The Syrian and Newton's hamsters are included in the International Red Book.
- Hamsters cause damage to agriculture as they feed on legumes and grain crops. In addition, they are carriers of pathogens of a number of infectious diseases, which is why their keeping is prohibited in Vietnam. The maximum fine for violation is 30 million VND, which is equal to the annual income of a resident of this country. But hamsters also bring benefits. For example, the skins of certain types of hamsters are harvested. Hamsters are also used as laboratory animals and pets.
Ways to fight and protect
Nowadays, both modern methods of combating and protecting against these rodents, as well as proven old ones, are used. Here are the main ones:
- Flooding holes . You need to find all the exits, barricade them and pour water into the hole until the animal crawls out of the only hole. There you can catch him. Minus: be careful that you have found all the emergency exits from the hole, otherwise the hamster will hide.
- Digging holes and catching by hand . Disadvantage: very labor-intensive and dangerous.
- Domestic animals , cats and dogs, hunt rodents. Minus: hamsters are very large, not every cat can handle it. And a dog can trample the entire garden. In addition, the hamster can bite them and infect them.
- Various traps , live traps. Cons: It can be difficult to keep track of where it can get out and where to place them.
- Spreading poisoned baits . You can use rat and mouse poison. Minus: it is not a fact that the majority of individuals will eat it, especially since the number of pests is quickly restored.
- Use of noise and ultrasonic repellers . Disadvantage: it is difficult to place them over a large area and quite expensive.
The big problem is that hamsters are very active and cunning animals, and also fearless. Catching or scaring away a hamster in the countryside is not so easy.
Dear gardeners and gardeners! You must definitely try all the ways of fighting and destroying until you achieve success!
Otherwise, you risk not only being left without a harvest on your farm, but also your own health and life, as well as your loved ones!