Feeding young rabbits
Feeding young animals, like feeding animals of other economic groups, has its own characteristics. Let's look at some of them.
First of all, it should be noted that young animals should be separated from female rabbits no earlier than 30-45 days of age. At this time, the apparatus for digesting food in rabbits is not yet sufficiently developed and is simply not adapted to process large quantities of food. That is why it is necessary to introduce highly nutritious and highly digestible food into the feeding rations of rabbits - young green grass or vitamin-rich hay of legumes and legumes, oats, boiled potatoes, carrots. It is advisable to feed the concentrates themselves in crushed form (compound feed). From animal feeds, you can feed baby rabbits whey, milk, bone meal, fish meal and meat and bone meal.
After jigging, the rabbits eat the same food that they received when they were with the rabbit. Unfamiliar foods should be introduced gradually. You need to start with small doses. Feeding rates and rations can be increased approximately every ten days.
When raising young animals, good results can be obtained by feeding granulated feed. When your pets are 46-60 days old you can give them approximately 85-125g of complete kibble, at 61-90 days 130-170g and at 91-35 days 170-200g.
A rabbit's diet can also consist of 85 percent complete pellets, with hay and green feed accounting for 15 percent of the total nutritional value. These figures can be attributed more to the feeding of young animals and males. If you have replacement young animals, then it is advisable to add green and roughage to the pellets in an amount of 15-30 percent of the total diet.
Rabbits need to be fed two to three times a day. In the morning, you can give them half of the daily portion of the necessary concentrates: in the afternoon - give hay or their favorite grass, in the evening - the rest of the concentrates, root vegetables, silage
If you use pelleted feed, you only need to pour it into the hopper feeders once a day. Hay and grass are distributed as they are consumed.
Feed storage
To obtain greater benefits and material benefits, you need to think about the proper storage of feed and prevent its spoilage.
The main problems of improper storage:
- Infestation by harmful insects and mold. The bran and grains included in the composition are a favorable environment for them.
- Loss of nutritional properties of vitamins and minerals.
- Poisoning or infection of animals in the presence of harmful bacteria.
To prevent such phenomena, special conditions for storing feed are created in livestock farms. Some of them can be used in small farmsteads:
- the presence of a dry, ventilated room;
- avoiding dampness and direct sunlight;
- fight insects and rodents;
- read and follow manufacturers' recommendations;
- observe the expiration dates of the feed.
Feeding lactating rabbits
Feeding lactating rabbits differs from any other feeding of farm animals in that their diet requires the introduction of food that will be distinguished by its juiciness and variety.
The best food will be: in summer - green grass (legumes or cereals); in winter, forb hay, silage, potatoes, roots and tubers.
In the feeding ration, the share of concentrates is increased to 60-70 percent (depending on the nutritional value of the diet). Rabbits happily eat wheat bran, peas, sunflower cake (60-80g), feed yeast (5g), bone meal (3-4g). Feeding rates should be increased from the 20th to the 45th day of lactation. In the end, it is worth noting that for each baby rabbit in winter you need to add 30g of concentrates and 20g of hay; in summer - 25g of concentrates and 60-100g of grass.
Feeding pregnant rabbits
I advise you to pay great attention to the feeding diet of pregnant rabbits and here’s why. If the mother's body lacks nutrients, the normal development of the fetus is delayed. That is why the diet of nursing rabbits should contain both oats and mixed feed, legume grains (80-100 g); As a protein feed, you can add sunflower cake or meal (30-55 g), soybean meal (up to 30 g). Juicy feeds include silage and carrots. Mineral feeds include chalk, bone or meat and bone meal (1-2 g). Don't forget about fish oil (2 g). Before breeding (approximately 5 days in advance), the amount of bulk feed is reduced, and the amount of concentrates required for nutrition is increased.
Feeding newborn rabbits
If the mother of the rabbits has died for some reason, or is capricious and does not want to feed her offspring, you can try to feed the newborn rabbits manually. Most often, when trying to feed baby rabbits with a bottle, they can die either within a couple of days, or at most within a week. Hand feeding itself does not lead to success, since mother's milk cannot be replaced one hundred percent.
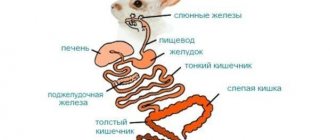
The most likely cause of death is mucous enteritis. It happens that rabbits that were fed by their mother get sick with it, but most often it can happen to babies who were weaned from their mother before the age of 8 weeks. Signs of this disease include refusal to eat, severe diarrhea, and blood and mucus in the droppings. The cause of colitis may be the active growth of bacteria belonging to the pathogenic group. It (the bacterium) can develop in the appendage of the cecum just when normal microflora begins to establish there. It is this microflora that helps babies switch from milk to more solid foods.
In the stomach of rabbits, the acidity level is pH 1-2p, but in newborn babies it is much higher. In recently born rabbits, the stomach and gastrointestinal tract are sterile (that is, there are no microorganisms in it). The acidity level of baby rabbits will gradually change when they switch from milk to solid food. This process will be helped by the components that make up mother's milk.
Ten days will pass and your rabbits' eyes will open. At this time, they begin to eat the mother's caecotrophs. Caecotrophs will provide your babies with the substances necessary for the development of their body, and then later, when they switch from milk to solid food, caecotrophs will help introduce microflora into the cecum, which is so necessary for metabolism.
Cecotrophs are clusters of dung balls glued together. These caecotrophs are similar in size and shape to the mulberry fruit. They are high in vitamins K and B, as well as protein and fiber. Therefore, caecotrophs are a very important part of the diet of rabbits, and they are eaten only after emerging from the anus. When feeding baby rabbits by hand, it is necessary to provide them with the caecotrophs of an adult animal. This must be done as soon as their eyes open. As a rule, babies begin to eat caecotrophs immediately. But, if you notice that babies refuse to eat caecotrophs, you should add 2 to 3 peas from a bunch to the mixture that the rabbits eat and provide them with such nutrition once a day for 3-4 days.
Even if your rabbits have switched to adult food, be sure to monitor their droppings. Having noticed the first signs of mushy stool, immediately start giving cecotrophs again. If necessary, add them to the mixture.
It happens that the cecum of rabbits, which is sterile, cannot be populated with adult normal microflora. This directly depends not only on the nutrition of the children, but also even on stress, which affects the immune system. In this case, unfortunately, pathogenic flora begins to increase in the cecum, which leads to bloating and death from mucous colitis.
Small rabbits can quickly lose their sucking instinct, and if you hand-feed them, you should start feeding them within the first two days. If the sucking instinct has disappeared, use an insulin syringe to draw up the mixture (after removing the needle). Make sure that the rabbits do not choke, make sure that your mixture is warmed up, the babies are warm to the touch, and the syringe and bottle are sterile. This is very important, because through an unsterilized bottle or formula that you have prepared incorrectly, you can introduce quite dangerous bacteria into the baby’s fragile body.
In addition, I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that caring for newborn rabbits includes providing warmth in a basket with soft wool filling and the presence of a heating pad. It should maintain a temperature of 68-72 degrees Celsius. This temperature will be optimal for their survival. You need to keep the basket in a quiet place with minimal noise and handle the rabbits only during feeding. For feeding, you can use a milk replacer for kittens. Add a tablespoon of cream there, which should correspond to the calorie content of natural rabbit milk. You can try feeding your babies evaporated milk or goat milk, adding three tablespoons of karo corn syrup and one egg yolk. While feeding, hold your baby on your lap, surrounding him with a soft towel. When your pets' eyes open after 10 days, you can start feeding them special pellets and hay. It is better not to give vegetables and fruits right away.
What not to feed
Rabbits are herbivores, characterized by their gluttony and omnivorous nature. At the same time, they are extremely sensitive to the quality of food, as well as its content. From the large number of possible products for feeding these animals, the following components that pose a health hazard should be excluded:
- red beets;
- rotten and moldy grass, hay and straw;
- poisonous plants and trees (hemlock, belladonna, lily of the valley, dope, spurge, apricot, buckthorn, wild rosemary, bird cherry and others);
- poor quality silage;
- sweets and baked goods;
- frozen or rotten root vegetables.
Hay made from marsh grasses is especially dangerous for rabbits. Regular feeding of such food can lead not only to digestive problems, but also death due to poisoning. Vegetables and fruits should be given in limited quantities.
Feeding rabbits at home
Any household can feed your pets economically. Why, you ask? Because rabbits will willingly eat cabbage, silage, carrots and other vegetables, as well as your existing melon and gardening waste. These feeds contain easily digestible carbohydrates and vitamins. You need to know that red beets and cabbage, given to rabbits in large quantities, cause diarrhea in rabbits. If root vegetables are frozen, they can only be fed boiled. Potatoes should be given to the rabbit boiled and mixed with bran or mixed feed. If your root vegetables are fresh, they should be thoroughly washed and fed to your pets in pieces.
Silage is a useful food for rabbits. These animals can be fed corn, sunflower, carrot and cabbage silage with the addition of potatoes, beets and coarse concentrated feed. Rabbits should be taught to eat silage gradually, starting from 25-100g
Roughage
From this group of foods, eared animals will happily eat straw, hay, as well as tree branches with leaves. Rabbits especially love legumes (clover, alfalfa) and legume-cereal hay. Useful and necessary food is forest, meadow, steppe hay and hay that was mowed before flowering or at its very beginning. If there is a lack of hay, you can include millet, oat or pea straw in the feeding diet.
For roughage, give branches of aspen, rowan, acacia, willow, linden, and maple. Alder or oak branches should be fed to rabbits if they have indigestion. They have a strengthening effect on the stomach. Rabbits also eat spruce and juniper branches (100-200g per day per head).
Concentrated feed
This group of feeds includes grain feeds (legume and cereal grains and oilseeds). Compound feed also belongs to this group. Grain feeds - oats, barley, vetch, lentils, peas, soybeans and others are valuable because they have a large amount of nutrients. To obtain good productivity, include at least 40-50 percent concentrated nutritional feed in your rabbits' diet. If possible, use a mixture of two parts oats, one part corn (or barley or wheat) and a small amount of vetch, peas or cake.
Legume grains can be soaked before use, and cereals and legumes can be given in crushed form. Before distributing, moisten bran, cake or crushed grain so that their dust particles do not affect the functioning of the upper respiratory tract of rabbits. You can feed them mixed with silage and root vegetables.
Corn is given to rabbits either soaked or crushed, millet is only hulled and brewed. Seeds related to oilseeds can be fed either whole or crushed. You can try replacing concentrates with acorns, previously peeled and ground (approximately 50 grams per adult rabbit per day).
Food waste
This type of food includes crusts of bread, crumbs from soups and cereals, potatoes and the like, which rabbits readily eat. Add bran, cake or mixed feed, crushed grain to the remaining soup, and then feed it to the rabbits in the form of mash. Such waste should comprise up to two hundred grams per head per day in the diet of adult rabbits.
Animal feed
This group of animal feed includes milk obtained from a cow (as whole milk, skim milk), whey, meat and bone meal, meat meal, and fish meal. Milk (both whole and skim), whey, and buttermilk can be fed to the rabbit along with mash (five to ten grams per rabbit per day). Whole milk can be given to young animals (five grams) and nursing rabbits. Skim milk is used in fresh and also fermented form, buttermilk and whey in natural form. Meat-bone, meat-based fish meal is a nutritious food that contains from twenty to sixty percent protein. It is introduced into feed mixtures in an amount of one to two percent.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
As a rule, a lack of vitamins and minerals is observed in rabbits in winter and early spring . There are several vitamin and mineral complexes that are very successfully used by rabbit breeders:
- "Chiktonik" - includes about three dozen vitamins and basic amino acids. The drug is given in five-day courses, every month, at the rate of 1 ml per liter of clean water;
- “Prodevit” is a vitamin complex designed for weakened animals suffering from ulcers, rickets, liver diseases, and pathology of the mucous membranes. The drug is available in injection and oral form;
- “E-Selenium” is a drug intended for the correction of developmental and growth disorders, exacerbation of infectious diseases, treatment of poisoning and other pathologies. Available in injection and oral form.
Mineral supplements represented by mineral stones: “Chika” and Karli have proven themselves very well. You can also use "Bio-iron", supplemented with essential microelements, and the vitamin and mineral supplement "Ushastik".
Return to content
Feeding rabbits in winter
Often your pets may experience vitamin deficiencies in winter or early spring. Along with food, rabbits must be given vitamins of the ADE group, and in some cases even B12. All other vitamins will be synthesized in their body. If you give your rabbit good hay, silage or fermented green food in winter or spring, then the rabbit’s body will fully provide itself with vitamin A. If the hay is bad, then feeding rabbits in winter will require you to add vitamin A concentrate-250ME per kilogram to the food. live weight in (mash). Also, a source of vitamins A and D can be fortified fish oil: for young animals - 0.3-0.5 grams, for adults in the non-breeding period - one gram; for pregnant rabbits - two grams, for nursing rabbits - three grams per head per day. If you are looking for a source of carotene for your pets, then look no further than pine and spruce branches.
A rabbit can get a lot of vitamin E from sprouted grains. It is given to adult rabbits per head per day. Baker's yeast is also rich in vitamin E. You can give four to six grams of yeast per rabbit per day for five days, then take a break for three days. Throughout the year, the animals' diet should include table salt. Adults - 1-1.5 grams; for young animals 0.5-1 gram per day per head.
Also use bone meal and fish ash, chalk, and feed phosphate. These products belong to mineral feeds. There should be one to four grams of them in a rabbit’s diet per head per day.
Now let's talk a little about succulent food. You can ferment them for the winter. Chop cabbage, turnips, herbs (preferably legumes). Immerse the carrots in barrels, sprinkle them evenly with table salt at the rate of one or two percent by weight and compact until the juice appears. Then place a wooden circle on top and a weight on it. For an adult rabbit, there should be no more than three hundred grams of such feed per day, for young animals - one hundred grams per head. When feeding silage and fermented succulent food, be sure to give the rabbits chalk at the rate of one to four grams per hundred grams of feed.
Diet during mating
To get healthy and strong rabbits, you need to take care of the condition of the future parents. Thin people are provided with enhanced nutrition, and fat people are put on a diet. Too little or too much fat leads to stillbirth and reduces sperm quality in males.
Enhanced feeding of exhausted individuals begins a month before the mating period. It is necessary to increase the daily diet, bringing it closer in nutritional value to the menu of pregnant women. Abundance and variety are complemented by multivitamins.
To improve sperm quality in males, you need to use protein foods. To enrich food, oilseed cake, meat and bone meal and fish meal are added. During the mating period, you should not use products that contribute to obesity, therefore exclude:
- barley;
- corn;
- potato.
The viability of the rabbits depends on the health of the producing animals. It is advised to provide a nutritious and varied diet with a sufficient amount of useful microelements. Veterinary supplements can be used at this stage.
What should a rabbit eat during the rest period? A typical diet consists of one-third grain and 70% hay. Added to food (in grams per head):
- salt - 1;
- bone meal - 4;
- ground shells - 2.
Basic feed
Basic feed (green feed) contains many nutrients. Rabbits eat them with pleasure, and they are well digested. Legumes and legume-cereal grass mixtures are valuable for rabbits. These include clover, sainfoin, alfalfa, vetch and oatmeal mixtures. If you include these herbal mixtures in your rabbits' diet, you can reduce the amount of grain you provide and reduce the cost of feeding your rabbits.
Of the wild herbs, long-eared herbs like to eat nettle, burdock, yarrow, tansy, dandelion, wormwood, mother and stepmother.
The rabbit loves almost all steppe and meadow grasses. If possible, try to include a variety of herbs in your rabbit's diet.
In the spring, grass should be introduced into the rabbits' diet little by little, starting with small doses. It is best to feed freshly cut grass to rabbits, but if the grass you cut is wet, dry it on racks or under a canopy. Adult rabbits can be given 1.0-1.5 kilograms of grass per day, and young rabbits 150-500 grams.
When you feed wild herbs to rabbits, make sure that they do not include plants such as hemlock, poisonous weed, foxglove, caustic buttercup, henbane, lumbago, and crow's eye.
When feeding rabbits in the fall, you can not forget about the tops of carrots, turnips, cabbage leaves and other crops grown in your garden. Green potato tops are fed a week before you decide to harvest the potatoes and give them to rabbits dried or fresh. If you feed rutabaga tops, cabbage leaves, or beets to rabbits, be careful! Your pets may experience bloating. To prevent this from happening, wash the tops from dirt and hang them on racks. When feeding rabbits, tops taken from the garden must be introduced gradually, in small doses (young animals - thirty grams, adults - one hundred and fifty grams.)
So in this article we tried to look at how to ensure that feeding rabbits contributes to their rapid growth and proper development. We hope that by following all the recommendations outlined above, you will not only get healthy offspring, but also spend time usefully, watching how your animals happily gnaw on the treat you brought to the feeder. Preparing feed and feeding itself, of course, requires both material and physical costs, but once you decide to breed rabbit offspring, try it, don’t be lazy and go ahead.
Cooking methods
You can prepare grain for feeding rabbits using several methods: steaming, yeasting, germination, crushing.
Before you start cooking, be sure to inspect the grains used:
The grains should not contain dirty seeds, small stones and green unripe grains
You also need to pay attention to the presence of small insects or fungal spores; they should not get into the food of rabbits. If black spots are visible on the grains, they should not be used to feed animals. Do not feed overdried or raw grain to rabbits. Grains must be steamed before serving to rabbits.
Cereals must be steamed before serving to rabbits.
Steaming
Steaming is the simplest and at the same time very effective way of preparing grain crops for feeding rabbits.
For steaming, take grains of one type or pour the prepared mixture of cereals into a bucket or other container, but not to the very edge, since during the steaming process the volume of the resulting mass will increase. The grain is poured with boiling water. You need to add 1 tbsp to the water. salt, then stir the mixture and cover lightly with a lid. The container should be left in this form for 5 hours. During this time, the grains will swell and can be used for feeding.
Steamed grains become soft and sweet, the digestive system of animals copes better with such food, and nutrients are absorbed faster. Rabbits eat this food with pleasure.
Yeasting
This method of preparing feed is used to accelerate the growth rate of animals and rapid weight gain. It can be used for rabbits starting from 4 months of age. Preparation proceeds as follows:
- The grains are ground and mixed in a container with water in a ratio of 1:2.
- Yeast is diluted in water at the rate of 36 g per 2 liters of water.
- All components are thoroughly mixed and left overnight.
- The whole process takes about 6-9 hours. From time to time the mass needs to be stirred.
When feeding, add 2-3 tablespoons of yeast mixture to the dry cereal mixture at each meal. This regime is maintained for 5 days, after which the food is changed.
Sprouted grains are much healthier than dry grainsGermination
Sprouted grains are much healthier than dry grains due to the fact that during the germination process they release beneficial substances that are not absorbed by the body when dry grains are consumed. Swollen fiber perfectly cleanses the animal’s intestines, removing accumulated waste products from the body, and also increases the body’s protective functions.
When preparing food, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- The grains selected for cooking should be pre-washed in warm water. If you immerse grains in water, you will notice that some of them float to the surface. Such grains cannot be used as food for rabbits; they are already considered dead.
- The grains should be washed several times to prevent fungal spores from getting into the feed. During the growth of grain crops, enzyme poisons are released that are detrimental to animal health.
- If silver water is used when washing grain, and not ordinary drinking water, then there is no need to repeat the procedure several times.
If food needs to be prepared for a small number of animals, then you can germinate the grains in a plate, placing them in a damp cloth, and you need to regularly add water to the grains to maintain the moisture level. On large farms, feed is prepared in buckets, filling the grains with water up to 2 cm from the edge.
The whole process consists of the following steps:
- The grains filled with water are left for 12 hours, during which time they will swell well.
- After 12 hours, the grains are transferred to plastic bags, in the bottom of which holes should be cut so that all excess moisture is drained from the grains.
- The bags are placed in a warm place. The grain layer should not be higher than 8 cm.
- The mixture can be fed to rabbits when sprouts become visible in it.
Crushed grain
Another method of preparing feed is crushing. You can purchase the cereal mixture in this form, or you can prepare it yourself. To do this, you just need to grind the prepared culture. Typically, corn is crushed, but oats, wheat or barley can also be prepared this way.