- home
- Guinea pig
- General information about guinea pigs
02/18/2019 For people, vision is one of the most important senses of perceiving the world. But is this true for guinea pigs? Can animals go blind and continue to lead a full life? The information presented will help you find out how these animals see the surrounding reality, and what needs to be done to preserve their vision.
Guinea pig visual organs
First of all, it is worth noting the presence of fairly large eyes on the sides of the animal’s head. Thanks to this peculiarity of the location of the eyes, the animal can see what is happening from a greater angle than a person. Also, such a radius of vision of the animal allows it to instantly detect danger and react to it. Despite the fact that the pet's vision has not been fully studied, many signs make it clear that he can see objects in color. It is able to distinguish a range of shades and also reacts to moving objects.
A special feature of a guinea pig's eyes is that they can simultaneously see objects to the right and to the left of themselves.
According to recent research, pigs can distinguish the following colors:
- green;
- red;
- blue;
- yellow.
This vision feature helps the pet better distinguish food. Myopia is considered another congenital feature of a pet, therefore the emphasis in the process of survival is often placed on other organs, for example, hearing or smell, but these organs will be discussed below.
What colors does a rodent distinguish?
As a result of research in the field of rodentology, scientists have proven that guinea pigs have color vision that is more developed than that of dogs and cats. Pigs have several primary colors, namely: green, yellow, blue and red.
They use this ability to determine the edibility of food. For example, if you put a leaf of lettuce without a herbal smell in the cage, the pig will find it without problems, focusing on the color of the greenery.
Ways to see a pig in the dark
Like other rodents, guinea pigs have good orientation and vision in dark rooms. Despite the virtual absence of helplessness at night and the ability to perform basic operations, vision in rodents is still considered daytime. Because of this, it is ideal to place the cage in a well-lit area, but away from direct sunlight. Experiments have been conducted to prove the negative influence of darkness on the animal. Degradation, disease, and mutations of various types occur. It has been noted that in the process of survival, animals are better oriented in space thanks to hearing and smell rather than vision.
Origin
The animals are of South American origin. Pigs living in natural conditions are most widespread in Peru and Chile. In the territories of these countries, wild rodents are found:
- in forests;
- in the wastelands;
- in rocks, etc.
It was from South America that pigs came, thanks to Columbus, to Europe. Europeans quickly fell in love with the strange animals and soon turned from an animal with delicious meat into pets.
In the scientific world, these rodents are designated by the Latin word “cavia”. The name “guinea pig” was assigned to the animals not by scientists, but by ordinary people. “Pig” - because it grunts. “Sea” - because she arrived from the other end of the world, from across the sea.
Domesticated animals do not like water. They should be bathed as rarely as possible. And even more so, you shouldn’t let the animal just swim. Once in the water, a land rodent experiences stress and may even drown or choke from fright.
Possible problems with the organs of vision
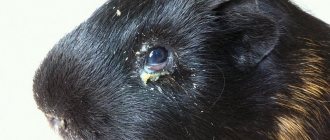
Despite the poorly developed organs of vision, pigs have no problems with it. This does not happen often and is usually a side effect of respiratory diseases. Such problems can also indicate diabetes, dental disease and general dehydration of the animal. A sign of vision problems is the presence of discharge from the eyes, and the pupil becomes cloudy. The quality of general vision decreases, the animal is less oriented in space.
Due to damage to vision, the animal may begin to develop a corneal ulcer. If the rodent's eyes are swollen and watery, and the animal itself behaves restlessly, you should consult a veterinarian. Cataracts are age-related changes or a consequence of diabetes. Sometimes animals are already born blind, but thanks to well-developed other organs and with a high-quality standard of living and care, they are no different from their brothers.
Viral diseases
What diseases in guinea pigs can be caused by viruses? The most dangerous viral pathologies are paralysis and pestilence. Such diseases are manifested by convulsions and paralysis of the limbs. The animal must be taken to the veterinarian immediately.
Symptoms of other viral diseases include:
- diarrhea;
- matted fur;
- unusual behavior;
- nasal discharge.
Among the bacterial diseases, it is worth noting pseudotuberculosis, in which the guinea pig experiences frequent diarrhea, causing severe exhaustion. This disease is contagious, so the animal must be isolated so that the others do not die.
Timely vision testing and care
The initial vision test and consultation should be with a veterinarian. In order not to start the process, you need to pay as much attention to your pet as possible. If problems are detected, you should immediately contact your veterinarian.
The more often the owner has contact with the animal, taking it in his arms, the sooner and more timely it will be possible to detect the following signs:
- cloudy pupil;
- film formation;
- redness of the eyelids;
- discharge from the eyes;
- rolled up eyelid or its unnatural position;
- unnatural protrusion of the eyeball.
You can check an animal for blindness by bringing an object to it in an unexpected way. If the animal sees, at a minimum it will react to the danger and twitch. In blind pets, the reaction to danger and the instinct of self-preservation do not work.
Because the pet’s vision is not very good, it is important for the owner to remember several basic criteria for creating proper care:
- If you suspect vision problems, you should immediately, without delay, go to the veterinarian. And do not speculate and prolong the course of the disease. The activity of the animal does not mean good vision. In the surrounding world, pigs navigate with the help of other organs, which misleads owners, especially inexperienced ones.
- It is not recommended to place the cage in a too dark place, or under a lamp. Direct sunlight on the cage also negatively affects the animal's vision.
- Observe the animal more carefully, especially in open spaces. If there is blindness, but it is not detected, the animal can harm itself.
In addition to vision, the animal has other developed organs, but much better.
Hygiene
Rosette pigs have coarse fur that requires grooming. The rodent's ears also need special attention. The rest of the care includes standard procedures for rodents.
Wool
The fur needs to be combed approximately once every three days. To do this, use a comb and a massage brush with natural bristles. Some breeders recommend wiping the rodent's fur with a damp cloth once a week.
Bathing
Rosette guinea pigs are bathed only when absolutely necessary, if it is not possible to remove dirt from the fur in any other way. To wash a rodent, you will need a basin or bowl with sides no more than 43 cm high.
The most difficult thing in this matter is to wet the rough hair of the rosette pig and rinse it well. You will have to be patient, because the rodent will most likely be against water procedures.
Animal shampoo is used to wash fur. If you don’t have one at hand, this product is suitable for infants, as it does not dry out the skin and does not cause allergies. After bathing, the rosette pig is blotted with a terry towel and placed in a warm place. It is advisable to close the windows (even if it is warm outside) so that the rodent does not catch a cold.
Ears
Rosette pigs cannot clean their ears on their own, so you will need human help. Once a week it is necessary to inspect the inside of the sinks. If a lot of sulfur has accumulated there, it must be removed with a cotton pad soaked in a special lotion for animals.
Claws
Rosette pigs need to have their nails trimmed periodically, otherwise they will curl up, which can lead to pododermatitis and crooked toes. A cat nail clipper is suitable for trimming. The procedure is carried out approximately once a month, when the length of the transparent part of the claw reaches or exceeds 2 mm.
Before you begin, you should choose a well-lit area. If the rodent breaks out, you can wrap it in a towel or blanket. Only the tip is cut off (no more than 1 mm) so as not to touch living tissue. Otherwise, bleeding will begin and the wound will become infected.
Cleaning the cage
The health of a rosette pig depends on the conditions in which it lives. It’s not enough just to furnish her home; it needs to be kept clean. The litter becomes contaminated with feces and urine, and an unpleasant odor appears. It is advisable to replace the filler after 5-7 days.
To do this, all the equipment is taken out, and the rosette pig is removed. The tray is thoroughly washed with hot water. Do not use any detergents or cleaning products other than baking soda. The feeder is emptied of its contents, washed and scalded with boiling water. The water in the drinking bowl is replaced with fresh water. Cleaning is also done in the sleeping house.
Olfactory organs
The main task of the olfactory organs is to help the pig communicate with relatives and find a mate to satisfy sexual instincts. Like many mammals, in pigs urine plays the role of marking territory and attracting partners of the opposite sex. In males, urine means a call for mating, while the female may respond by refusing the male. First of all, animals are guided by their olfactory organs and are able to recognize each other in a pack by smell. Shy behavior when meeting people is the norm for guinea pigs. Pigs have a more acute sense of smell than humans. It is developed 1000 times more powerful than in ordinary people.
Possible pathologies
Guinea pigs' eyes are not protected; they do not have nictitating membranes, which makes them vulnerable to various diseases.
The most common eye pathologies are:
- Cataracts (or clouding of the lens) that develop in older pigs (over 5 years of age).
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory phenomenon of the mucous membrane, as a result of which purulent discharge appears, the exudate dries out, crusts form, stick to the fur, and the eyelids stick together. The disease can be contagious if several animals live in the house and constantly communicate with each other.
- Corneal ulcer. Occurs when a mechanical injury to the eye occurs and there is no treatment.
- Blindness from birth is rare, but it is associated with defects in animal breeding.
- Fat eye is a hereditary pathology, characterized by protrusion of the eyes from the orbit, and cannot be treated.
- Retrobulbar abscess is an inflammation that develops when teeth grow into the eye socket. Occurs when improper feeding and the absence of hard objects to grind down the teeth in the animal’s cage.
Organs of touch
The organs of touch in pigs are the antennae located on the muzzle. These antennae help the pet navigate even in the dark and sense danger nearby. While an animal's sense of smell may fail, they can easily detect food or the presence of obstacles using their sense of touch. At the same time, along with instincts, the animal uses previously accumulated experience. For example, it easily distinguishes high-quality food from unsuitable food. By the way, it was thanks to this feature that it was possible to establish the animals’ love for sweet food.