When your guinea pig begins to itch, it indicates the presence of allergies, parasites or fungi. We are talking about systematic repetition; scratching once does not mean anything. If the animal’s behavior has changed, it has become lazy and even apathetic, there is loss of appetite and shedding, this is a reason to contact a veterinarian. Only he can say with certainty why the guinea pig is itching.
When should you sound the alarm?
All guinea pigs itch, this is a completely natural process - this is how they take care of their own hygiene. A pet may well scratch any place just like that, this is not a reason to sound the alarm. However, it is worth highlighting some factors that should alert the owner:
- The pig is constantly scratching one place.
- Dandruff is visible on the skin.
- The pig has become inactive or too irritable.
- Red spots, swelling, and black dots are visible on the skin.
- The hair began to fall out in places.
- Guinea pig bites itself and itches.
Any of these points, either individually or in combination with others, may indicate health problems for the guinea pig. Below we consider the main possible causes of scabies.
What should be of concern
Guinea pigs usually want to remove fur or relieve mild itching. However, you should be careful if the animal repeatedly scratches the same area or bites itself. Warning signs include:
- Formation of receding hairlines (not to mention the natural lack of hair behind the ears and inside the forelimbs);
- pet depression or anxiety;
- loss of appetite;
- strong thirst;
- dry skin, dandruff;
- formation of ridges, scabs, abscesses;
- inflammation of skin vessels.
The cause is often visible to the naked eye: parasites such as mites or lice are present in the fur. Sometimes the problem lies in internal pathologies of the body: vitamin deficiency, allergies, intestinal parasites.
Parasites
A guinea pig may itch severely due to infestation with scabies mites. It settles in the deep layers of the skin and causes unbearable itching. The guinea pig begins to scratch its skin until it bleeds, the hair falls out, and pustules form. A guinea pig can become infected through food, hay, from other animals and even from people.
Another unpleasant parasite is the lice eater. With the help of a magnifying glass it can be seen on the skin of an animal. The pig's hair falls out, itching begins, and dandruff appears. The disease affects the back, perineum and croup. Mumps can become infected through food and from infected animals.
Severe scabies can be a symptom of a lice infestation. The pig's skin turns red and peels. The animal begins to behave strangely: jumps up, squeaks, and itches very much. You need to look for lice on the head and ears.
One of the most common parasites that affects guinea pigs is fleas. They bite pigs, causing them to itch. Flea bites can cause severe anemia. The pig loses its appetite, becomes lethargic and inactive.
Is your guinea pig itchy, eating little and drinking a lot? Perhaps she has worms. The parasite is very dangerous for guinea pigs. The animal begins to lose strength literally before our eyes, problems appear with the digestive system, in particular with the intestines.
What can you do at home?
Mild diarrhea. The general condition of the animal is good, but the droppings are thin and light. Eliminate green and succulent food from your diet; instead, give hay and warm chamomile tea, as well as willow branches and grated carrots. Make sure the litter is dry. If the droppings are not hard after two days, contact your veterinarian.
Constipation. If the so-called perineal pocket around the anus is filled with feces, gently squeeze it out and remove it with a damp cotton swab. If small, hard balls of stool appear, first check whether the drinking bowl is functioning correctly, since in most cases the cause of constipation is simply not enough water in the automatic drinking bowl. For several days, eliminate grain food from the diet and give your guinea pig cucumber or melon. If there is no improvement within 24 hours, contact your veterinarian. Allergic runny nose. Eliminate possible causes of this runny nose, such as dusty hay or harsh cleaning products that produce fumes. If in doubt, contact your veterinarian.
Heatstroke. If your guinea pig begins to move restlessly from side to side, itches and trembles all over, immediately place it in the shade and offer water at room temperature. The body should be carefully wrapped in a cool, damp towel, and the animal should be calmed with gentle stroking.
Guinea pig diet. If your guinea pig begins to gain weight, you need to put it on a diet. Fat animals are slower and more susceptible to disease. Give the animal only 40-60 g of succulent food per day and reduce the dose of the main food. Let your guinea pig go for walks often. Make her do various “exercises”, for example, put the lettuce on some elevation or place an obstacle on the way to the feeder so that the animal is forced to climb for food.
Veterinarian at home SAO
Refusal of food. Sometimes it happens that due to some illness a guinea pig refuses to feed. Only a veterinarian can answer the question of whether it can be cured with forced feeding. Refusal to feed has various reasons.
Misaligned teeth or bite problems are a serious hindrance to eating for guinea pigs. If the incisors and molars are incorrectly positioned, they grow continuously, and the animal is simply unable to take food.
A guinea pig may starve due to missing its mate, which can lead to its death. In most cases, a guinea pig, left alone, is very worried, sits in the corner of the cage and does not eat anything, because it cannot bear the loss of a friend. Even if she does not refuse food, this does not mean at all that the animal feels well. In any case, it is better to add a new partner to her. She will probably enjoy the company of a young guinea pig aged 6-10 weeks. As the animals get used to each other, act carefully and give them the opportunity to establish contact.
Note. Do not try to replace your guinea pig's lost friend with yourself, as at one point you will feel that this is too burdensome for you, and the guinea pig will certainly suffer from this.
Allergy
Scabies can be the result of an allergy. The animal can scratch one place until wounded, its hair falls out, its eyes water, there is sneezing and shortness of breath. The cause may be a food allergy or an allergy to bedding.
The immunopathological process can be caused by pine sawdust, which releases substances that irritate the respiratory tract. Constant contact with skin and fur can cause a severe allergic reaction over time. If your guinea pig shows signs of allergies, you need to change the bedding to cellulose or corn.
If a guinea pig has a food allergy, identifying the exact source is not so easy. It is advisable to get tested. However, you can also try to determine the source of the problem at home by combining different foods and carefully observing the animal. The component that causes an allergic reaction should be completely excluded from the diet.
Types of shedding in guinea pigs
Hair change is a normal process that occurs in most mammals.
Natural juvenile molt
Juvenile or age-related molting occurs in an animal only once in its life, when it passes from childhood to adulthood. This is a completely normal and safe phenomenon, during which, instead of soft fur, a permanent, harder and denser one appears.
Seasonal molting in rodents
Seasonal molting is provoked by changing seasons and temperature conditions. In nature, guinea pigs shed twice a year. Autumn or summer molting occurs quickly, and often the owner does not even notice it. The process does not cause any inconvenience to the animal.
But in the spring, starting from March, changing fur can cause a lot of trouble. Often during this period the pet experiences discomfort and is nervous. In winter and spring, the guinea pig's diet contains little plant food, so the rodent does not receive the necessary vitamins and minerals. Dry and warm air due to the operation of heating devices in the apartment can also negatively affect the condition of the pet.
To help the animal, you need to:
- replenish the supply of vitamins with the help of supplements and special vitamin complexes;
- if possible, add fresh vegetables and fruits to the animal’s diet;
- ventilate the room (while ventilating, take the cage with the rodent to another room so that it does not get sick);
- humidify the air in the room.
Features of seasonal molting in domestic pigs
Animals living in an apartment do not have the ability to determine the season, since the air temperature in the room stays at approximately the same level all year round. In such conditions, the animal’s natural rhythms are disrupted. Therefore, domestic pigs can shed at any time of the year, and not just in a certain season.
Shedding may be due to poor nutrition
Fungus
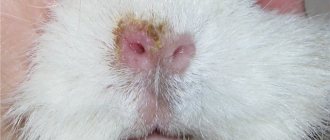
A guinea pig may itch due to shingles. Most often it can be seen on the face. Without treatment, it spreads throughout the body. If a flaky spot appears on the skin, hair falls out, a wound has formed, and the guinea pig often scratches it - perhaps the cause is a fungus.
A guinea pig can catch shingles from other infected animals. Also, the reasons for its appearance can be stress, age, too high humidity in the cage, wet bedding. Ringworm can also appear against the background of other diseases. For example, against the background of allergies or parasite infection.
Viruses and bacteria
If a guinea pig is affected by a viral or bacterial infection, it requires emergency veterinary care. Since such diseases are dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the pet.
The most dangerous viral diseases include pestilence and paralysis of guinea pigs. Both diseases are accompanied by paralysis and cramps of the hind legs. If you don't want your pig to die, you need to take immediate action and take her to the vet.
Other diseases caused by viruses are less common. They can manifest themselves through diarrhea, baldness, cough, runny nose and purulent nasal discharge.
The first step is to move the infected pig into a separate cage, otherwise infection of other animals is inevitable. For viral and bacterial infections, the animal must be treated with antibiotics. Your veterinarian will tell you which is best.
Vitamin deficiency
Another cause of scabies can be vitamin deficiency, which is associated with a poor diet and lack of succulent plant food. The animal begins to develop scabies, a rash appears on the skin, and hair falls out. The pig is inactive and suffers from constipation. All this can result from a lack of vitamin C in food.
It is necessary to take the animal to the doctor to rule out infection by parasites, fungus and allergies as possible causes of scabies. If the doctor diagnoses Autominosis, it is necessary to increase the amount of food containing vitamin C. For example, you can hang a bunch of parsley rich in it in the cage.
Bad habits
There is another reason why an animal scratches and bites: boredom. Pigs are social animals and prefer the company of their peers or other pets. Therefore, they are usually included in homosexual pairs, unless there is an intention to breed or spend money on sterilization. If it is not possible to keep two pigs (they will need a larger cage), you should buy rodent accessories for your pet or increase the number of walks in the fresh air.
There are many reasons why a pig may experience itching and hair loss. None of them will leave on their own. The owner’s task is to notice these symptoms in time and determine their cause. Your veterinarian can help you make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Also, do not forget about preventive measures to maintain the health of your pet.
Stress
Stress can cause problems with the nervous system, so the guinea pig will begin to itch, lose hair and lose appetite. There can be many reasons for this little animal's stress. One of the main ones is poor living conditions, due to which the guinea pig is constantly in an uncomfortable and irritable state. Stress can accumulate and result in serious health problems.
If a guinea pig chews on the cage, then the cage is too small for it: these animals are not that small, and therefore require space.
Other pets can cause stress. For example, cats who like to watch the rodent from the side, and in the absence of the owner are not averse to sticking their paw into the cage.
Constant noise and vibration can unnerve your pet, so there is no need to place the cage near speakers or a TV.
Infectious pathologies
Plague
A particularly dangerous viral disease of guinea pigs, characterized by high contagiousness and lethality. After infection, the incubation period usually does not exceed 3 weeks. Clinical signs:
- general weakness;
- convulsions;
- apathy;
- lack of coordination;
- paralysis of the hind limbs.
The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory testing, and the sick pig is immediately euthanized. No treatment has been developed.
Pseudotuberculosis
A common pathology with high mortality and the main symptom is diarrhea. The disease has nothing in common with real tuberculosis - the name is given due to the discovery of nodules in organs during autopsy, reminiscent of tuberculous tubercles. The main difference from true tuberculosis is the absence of lung damage.
Clinical manifestations:
- watery stool mixed with mucus and blood;
- loss of appetite;
- conjunctivitis is often observed;
- palpation reveals an enlargement of the mesenteric lymph nodes;
- in the terminal stage, convulsions are observed.
A test with pseudotuberculin is used as a laboratory diagnosis, but at the moment this option is available in a small number of clinics.
Treatment is also difficult - most often pseudotuberculosis in guinea pigs occurs in a fulminant and acute form. Therapy is reduced to the administration of antibiotics (tetracycline) in a loading dose, as well as the use of sulfonamides.
Paratyphoid
A common infectious disease of guinea pigs. Damage to the digestive system is noted: debilitating foul green diarrhea, suppressed appetite, tympany. A sick pet is characterized by general lethargy, tousled fur, and constant inactivity.
For treatment use:
- tetracycline antibiotics;
- sulfadimezine;
- antityphoid serum.
Improvements in content are also being monitored. Due to diarrhea in a guinea pig, you should clean the cage more often, provide the animal with easily digestible food, and do not limit drinking.
Pasteurellosis
A bacterial disease of guinea pigs and other animals, the pathology is also dangerous for humans. In pets it manifests itself as a respiratory infection:
- profuse catarrhal-purulent discharge from the nasal passages;
- guinea pigs sneeze and rub their nose;
- hard breath;
- wheezing sounds.
With complications, diarrhea, pustular and erythematous skin lesions develop. In the terminal stage, convulsions are observed. The disease is characterized by high mortality, especially among young animals.
On large guinea pig farms, any stock showing obvious clinical signs should be separated immediately. It is recommended to destroy animals in serious condition and dead. All livestock, including clinically healthy ones, are prescribed a course of antibiotics and sulfa drugs. Therapeutic and quarantine measures are lifted a week after the last case of clinical manifestation of the disease, and all premises and equipment are disinfected.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis
A viral disease of guinea pigs, characterized by high mortality. The infection spreads with mice; other animals can also pose a danger, so before adding a new pig to an existing one, a month-long quarantine should be carried out.
Pets experience high fever and general weakness. The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests, in which case the guinea pig should be euthanized. No treatment has been developed, and the virus is also dangerous for people.
Bordetellosis
Previously, the disease was registered exclusively in dogs as “kennel cough”; later cases of infection in cats, farm animals, and rodents, including guinea pigs, were identified. The wide range of susceptible animals makes the disease dangerous for pets. In guinea pigs it often appears after contact with other animals. Therefore, the main preventive measure is to prevent contact and timely therapy, vaccination and diagnosis of dogs, cats and other animals. Vaccine prevention of bordetellosis has also been developed in guinea pigs, but it shows little effectiveness and only reduces the severity of the pathology.
Pets experience characteristic changes in the respiratory system:
- sneezing;
- labored breathing;
- catarrhal-purulent discharge from the nasal passages;
- temperature increase;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- the head is often turned to one side - otitis media develops;
- appetite is reduced or absent;
- general lethargy.
Treatment is complex; the best results are achieved with the combined use of antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs:
- subcutaneous injections of baytril, intramuscular injections of gentamicin;
- sulfadimethoxine.
Specific therapy in the form of menthol inhalations and eucalyptus decoctions is difficult, so sodium bicarbonate in an amount of 0.1-0.2 g/kg, thermopsis or pectusin should be added to the feed. To support the heart, injections of sulfocamphocaine or caffeine, carboxylase are prescribed. Complex vitamin supplements are recommended.
Treatment
Have you noticed that your guinea pig is itching, what should you do first? It is necessary to carefully examine the animal and note any deviations from the normal state.
If your guinea pig is itching from stress, carefully analyze the animal's living conditions and eliminate all possible causes of anxiety.
But if the causes of scabies cannot be visually determined, immediately take your pet to the veterinarian. He will take scrapings from the skin and send them for analysis. Only by determining the exact cause of scabies can the correct treatment be prescribed.
Allergic pig
Itching often accompanies a disease such as allergies. The pig itches, coughing, watery eyes, sneezing, and swelling of the eyelids. Allergies usually occur to food or bedding material (especially pine sawdust). If a pet has been eating the same food and sleeping on the same type of sawdust for many years, over time it may develop intolerance to these products.
Allergies cannot be cured. But in order to remove the symptoms, the animal needs to change food or bedding material. To determine what makes a guinea pig itchy, they are offered different foods one at a time. Symptoms appear a couple of minutes after contact with the allergen. Additionally, the pet is given antihistamines. In addition to food and sawdust, allergies are caused by tobacco smoke, dust, and pollen.
Prevention
Quite often, the reason a guinea pig becomes infected with parasites is through interaction with other animals. Pay attention to this. Walking an animal outside on green grass may not have the most pleasant consequences.
Guinea pigs can be kept together in same-sex pairs. If one of the pair gets sick, temporarily isolate the individual from the healthy animal. The cage, feeder and house must be washed thoroughly with disinfectants and dried. If you just bought a second animal from a pet store, temporarily quarantine it and monitor its health before introducing it to other pets.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of the cage. Pigs quickly contaminate the bedding with urine, which can cause irritation and inflammation. It needs to be changed on time.
At least once a month, you should inspect your guinea pig's body for wounds, irritations or inflammation. If you notice anything strange, you should immediately contact a veterinarian.
Fungal diseases
The next reason why a guinea pig goes bald is diseases caused by a fungus. These include lichen and dermatophytes. Both diseases most often begin to appear first on the face, then move to the paws, neck and spread throughout the body. The fungus causes severe itching, the formation of bald patches and purulent wounds at the site of scratching. Ringworm can not only be transmitted to humans, but also lead to the death of the animal. If the infection is severe, the itching can become so severe that the guinea pig loses its appetite and dies from exhaustion and dehydration.
Prevention of all fungal diseases is to maintain the required humidity in the room where the cage is located, regularly change the bedding and regularly treat the animal for skin and intestinal parasites, and high-quality food. When purchasing a new guinea pig, especially at a pet store, it is necessary to provide the animal with a two-week quarantine and only then place the pet with other animals. 14 days is a sufficient period to determine the presence of skin diseases and other abnormalities in the animal.
If your guinea pig gets sick and your veterinarian confirms the diagnosis, you need to start treatment as soon as possible. The sick animal must be separated from all the others, and the cage must be disinfected with any strong chlorine-containing solution.
To combat fungal diseases, treatment with Nizoral shampoo, which is sold in any pharmacy, is recommended.
Nizoral has proven itself in the fight against many types of fungus, it relieves inflammation and itching, and reduces peeling of the skin. Nizoral is applied to the affected areas of the guinea pig's skin for five to seven minutes, then washed with warm running water. It is strictly forbidden to bathe the whole animal - water procedures are extremely stressful for a guinea pig. In addition to Nizoral, Fungoterbin 1% cream helps in the fight against fungus. It fights against dermatophytes, molds, and yeasts. You can also use Thermikon 1% cream or a spray with the same name and composition. Both creams are applied to the affected areas of the skin two to three times a day. Fukortsin or Castellani also cope well with fungal diseases.