Types of feed
All rabbit food can be classified into one of three types:
- Roughage. These include grass, vegetable tops, cabbage, hay and tree branches. In winter, hay stored in the summer is fed as roughage. Roughage is the main supplier of fiber to animals.
- Juicy feed. These are root vegetables, silage, pumpkin, zucchini. As a rule, succulent feed ends up in the animal feeder during the winter. They serve as an essential source of vitamins, but are poor in fiber and protein. In lactating rabbits, large quantities of succulent feed increase the amount of milk.
- Concentrated feed. These include cereal grains and legumes, bran, cake, mixed feed, and animal feed. Concentrated feeds are rich in protein but poor in vitamins. With an increase in the dose of concentrated feed in the diet, the growth rate of animals increases.
Nutritional features and types of feed
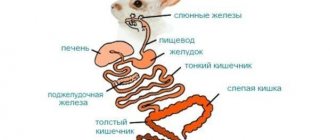
Rabbits have specific digestion. The stomach of animals has weak muscles. He cannot push food down on his own. Therefore, it must be constantly filled with food. And each new portion of food and water helps push food further into the intestines. This feature explains why the rabbit eats constantly (up to 50 times a day).
The rabbit's feeder should always be filled with food, and the rabbit's drinking bowl should always be filled with clean water!
To properly formulate a diet for long-eared gourmets, it is recommended to provide a variety of foods: green, rough, juicy, concentrated.
| Types of Rabbit Food | |||
| Green feed | Roughage | Juicy feed | Concentrates |
| •Wild plants • Seasonal grains • Garden green plants • Meadow grasses • Tops of vegetables (carrots, cabbage, radishes, beets) | • Hay • Straw • Branch feed | • Vegetables • Fruits • Silage | • Compound feed • Granulated feed • Mash |
Hay in rabbit nutrition
Hay is the most necessary and healthy type of food for a rabbit. It is given in unlimited quantities. The best option is hay made from meadow grasses, oats, and ryegrass.
Benefits of hay:
- contains many vitamins and healthy fiber;
- has good rigidity, which helps to grind teeth when chewing;
- the aroma of hay stimulates appetite;
- the animal eats such food in large quantities.
What branches can be given
Although interest in twig feed has dropped a little due to the frequent use of ready-made granulated feed, it has many positive aspects:
- saturates the animal’s body with natural vitamins, microelements, and organic substances;
- stimulates digestion;
- help grind teeth;
- excellent prevention of diarrhea;
- reduces financial costs for feed.
Trees whose branches are suitable for feeding rabbits In addition to the above-mentioned deciduous trees, branches of coniferous species (spruce, cedar, fir and pine) are used for feeding.
It is very useful for rabbits to eat branches with unopened buds in the spring. They contain an increased amount of valuable substances. It is recommended to give pine needles in the autumn-winter period. It is rich in phytoncides, which will be an excellent preventative against colds.
There are some restrictions when choosing branch food:
- Due to the high content of tannins in oak and alder branches, they are given with restrictions. They can cause a long-term fixing effect, but at the same time they will be an excellent treatment for diarrhea.
- Branches of cherries, sweet cherries, elderberries, bird cherry, apricot, wild rosemary, buckthorn, and wolf's bast are not used at all. The reason is the content of toxic substances in them.
What is compound feed, its advantages and disadvantages
Compound feed is a crushed and mixed mixture of plant and animal feed. During the cooking process, vitamins, macro- and microelements are added to it. For better absorption by the animal’s body, all components are selected according to their chemical composition, complementing each other. For each type of animal, feed is produced according to its own recipe.
Advantages:
- reduces time spent on feeding animals;
- easy to transport, convenient to store;
- feeding with compound feed makes the animal’s diet balanced, preventing health problems;
- the feed contains many components, thereby providing variety in animal nutrition;
- The vitamin premixes included in the feed save animals from vitamin deficiency.
Flaws:
- excessive amounts of feed leads to obesity in animals;
- compound feed – soft food. If they replace the bulk of the food, the rabbits' incisors will not wear down. This will lead to problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- the cost of purchased mixtures is quite high.
Main components
The basis of feed for rabbits of all ages is ground grains, of which the most preferred are wheat, oats, barley and corn. The grain group makes up 30 to 45 percent of the feed mass; Most of it is found in feed for lactating females and young animals.
The components of the second group of feed components are distinguished by their high protein content, which is necessary for the rapid growth and weight gain of the rabbit. These ingredients include: soybean and sunflower cake, wheat bran, soybean meal, hydrolyzed yeast, meat and bone meal. In addition, this group of components necessarily includes vitamin-herbal flour, which, in the absence of fresh hay in the rabbit’s diet, should account for half of the total feed volume.
Also, feed for rabbits may include meat meal and meal from inedible fish in an amount not exceeding 5 percent of the feed weight.
The third mandatory component of industrial feed for rabbits is a balanced vitamin and mineral complex, which includes chalk, tricalcium phosphate table salt, and a premix for rabbits.
When feeding rabbits with compound feed, it is also necessary to ensure that the animals always have clean, fresh water; and it is advisable to slightly moisten finely crushed grain for better absorption by the rabbit’s body.
Video about the best feed option for rabbits
Feed consumption rates
The norm depends on the age of the animal, physiological state and time of year. As a rule, there is usually a label on the packaging indicating how much of the product to give and to which animals.
According to the standards, for each animal it is necessary to allocate:
- adult rabbits – 180 grams;
- adult rabbits during the mating period - 230 grams;
- for female rabbits during pregnancy – 180 grams;
- nursing rabbits – 300 grams;
- young animals aged 1 month – 130 grams;
- at the age of 2 months – 150 grams;
- at the age of 3-4 months – 170 grams.
Compound feed is given to babies 5-6 times a day, to adult animals 2-3 times.
On a note! When feeding animal feed, animals must receive plenty of water.
Feeding rabbits on the farmstead of private household plots and peasant farms
How the owners of private household plots and peasant farms organize adequate feeding of rabbits will determine their health and, accordingly, the quality of the resulting rabbit meat, the quality of the skin and fluff. Owners should feed rabbits only high-quality, complete food. It is strictly forbidden to use low-quality food for feeding rabbits: moldy, blackened, musty, frozen, containing a large number of foreign impurities (weed seeds and poisonous grasses). All prepared food must be stored in a dry room, preventing insects and rodents from accessing it. Replacing one food with another must be done gradually over 5-7 days; Rabbit breeders should be especially careful when replacing dry feeding with succulent feeding and vice versa.
Features of feeding rabbits in different physiological periods.
Feeding adult rabbits during the resting period. The resting period in adult rabbits lasts from the laying of the young rabbits until fruitful mating, in males - from one mating period to another such period. At the same time, rabbit breeders must take into account that during the rest period, the rabbits’ body experiences the most minimal load, and accordingly, diets that ensure the maintenance of their life, preservation of live weight and health will be sufficient for them. A five-kilogram adult rabbit during the resting period requires 130-150 g of feed units per day; 12-16g of digestible protein, 1 g of table salt; 1.2 g calcium; 0.7 g of phosphorus and 1.2 mg of carotene (precursor of vitamin A).
During the feeding process, owners must ensure that their rabbits maintain their fatness and live weight. The diet for mixed feeding usually includes hay, succulent feed and approximately 40% of concentrates (in terms of total nutritional value), and for dry feeding - from 150 to 180 g of complete granulated feed.
Feeding rabbits during their preparation for mating and during it. The mating period is a crucial period in rabbit breeding. The success of the herd's reproduction depends on the readiness of the rabbits of the main herd for mating, and therefore proper feeding of the rabbits during this period plays a decisive role. By the time of mating, rabbits should be in a state of factory fatness. Their obesity and exhaustion are undesirable: in such a case, rabbits produce weak, non-viable offspring, and the quality of sperm in males sharply decreases.
In the case when the rabbits are poorly nourished, preparation for mating must begin 3 weeks before the start of the breeding period. In this case, a diet is used that is close in nutritional value to the diet of the pregnancy period per day (170-200 g of feed units and 13-16 g of digestible protein). The diet includes foods rich in protein (cakes, bran - approximately 20-27 g each), vitamins, especially A.E, D, as well as minerals (meat-bone and fish meal - 2-4 g each). It is important that the rabbits' diet is balanced in all nutrients. Rabbit breeders should not include in their diet foods that contain a lot of fiber and also contribute to the obesity of rabbits (barley, corn, potatoes).
Feeding pregnant rabbits . After mating, the breeding males can be switched back to the diet for resting rabbits. The diets of pregnant rabbits are increased in total nutritional value to 220 g of feed units per day. At the same time, per 100 g of feed units there should be 15-16 g of digestible protein. The diet of pregnant rabbits should include food rich in complete protein, minerals and vitamins.
In the first half of pregnancy, female rabbits spend a lot of nutrients on the formation of membranes, the placenta, and the embryo itself, which weighs about 3g. Proper feeding of female rabbits during preparation for mating and its implementation, as well as during pregnancy, has a beneficial effect on their fertility and live weight of rabbits at birth. Rabbit breeders should keep in mind that the diets of rabbits in the second half of pregnancy should not be too voluminous. 5-7 days before giving birth, the amount of roughage and grass in their diet must be reduced, while the amount of concentrates must be increased accordingly.
At this time, from concentrates, rabbits are given mixed feed, oats, legumes (80-100g); from high protein feeds – sunflower cake (30-55g), soybean meal (up to 30g); from juicy ones - carrots; from minerals - chalk, bone and meat and bone meal (1-2g), table salt (1.5g); of vitamins – fish oil (2g). The diets of young mature rabbits increase their overall nutritional value by 15-20% compared to the diets of older rabbits.
Feeding lactating rabbits . The rabbit's body experiences the greatest stress during lactation. Hence, lactating rabbits need to be fed abundantly and variedly throughout the suckling period. During the lactation period, a female rabbit produces up to 180 g of milk per day (sometimes more), which is necessary for the growth of the rabbits. Rabbit milk contains 34.2% dry matter, including 13% protein, 16.8 (sometimes up to 20%) fat, 2.4% minerals and 2% milk sugar. This high concentration of nutrients in rabbit milk explains the rapid growth of the baby rabbits themselves during the suckling period. To produce milk and maintain life, the female rabbit during the lactation period should receive approximately 2-4 times more nutrients in the diet than during the resting period.
With 6-8 suckling rabbits, the female rabbit needs at least per day: from the 1st to the 10th day of lactation - 330 g of feed units, from the 11th to 20th - 440, from the 21st to 30th - 560 and from the 31st to the 45th day of lactation - 700 g of feed units. Digestible protein per 100g of feed units of the diet during this period should account for 16-18g. To produce 1 g of rabbit milk, approximately 0.9 g of feed units are consumed.
The best food for baby rabbits during lactation is considered to be: in summer – clover, alfalfa, vetch-oat mixture, forbs; in winter - good forb or legume hay, potatoes, root crops, silage. From concentrates, rabbits are given oats, peas, cake, bran. The share of concentrates in the diet during this period is increased to 70-80% (in terms of total nutritional value).
Rabbits per day can be fed from 100 to 300 g of hay, from 40 to 60 g of sunflower cake, 30 g of sunflower meal, about 5 g of feed yeast, 3-3.5 g of fish oil, up to 3-4 g of bone meal and up to 7 g of meat and bone meal, 2 -3g chalk and 2.5g table salt.
To increase the milk production of rabbits, milk-containing (green, juicy) feed and concentrates are introduced into their diets.
Feeding the young . The most crucial period in the life of young animals is their weaning from the female rabbit. Typically, rabbit breeders separate young animals from female rabbits at the age of 30-45 days. It must be borne in mind that at this time the digestive apparatus of baby rabbits is not yet sufficiently developed and is not adapted to process large amounts of feed. Therefore, the diets of rabbits separated from their mothers should include highly nutritious and easily digestible food - young green grass or vitamin-rich hay of legumes and legumes-cereals, oats, boiled potatoes, carrots and some wheat bran. At this time, they can be given skim milk, fish meal, and bone meal from animal feed. Concentrates are best fed crushed or flattened.
Immediately after transplanting, rabbit breeders give the baby rabbits the same food that they received when they were under the rabbit. New types of food must be introduced gradually, starting with small cottages.
Young animals up to 3-4 months of age are characterized by the most intensive growth, and therefore the lowest feed costs per unit of live weight gain. Subsequently, feed costs increase by 2 or more times. At the same time, the diet should contain at least 16-17 g of digestible protein per 100 g of feed units of the diet.
Good results in the growth of young animals after weaning from rabbits are obtained by feeding them complete granulated compound feed for rabbits.
Fattening rabbits . Owners of private household plots and peasant farms who use complete granulated feed (dry type of feeding) realize to the maximum extent the tendency of young animals to intensive growth. With this feeding, rabbits at the age of 3-3.5 months reach a live weight of 2.5-2.8 kg. Full-age rabbits of reduced fatness, culled from the herd, are usually used for fattening, as well as young animals aged from 3-3.5 to 4 months, which by this time have reached the appropriate condition.
Fattening in rabbits consists of preparatory, main and final periods. When fattening full-aged rabbits, the first period lasts 5-7 days, the second - 8-10, the third - 8 days, and when fattening young animals, each of these periods is 10 days.
During the preparatory period, the share of concentrates in the rabbits’ diet is increased to 50% (in terms of total nutritional value), while correspondingly reducing the share of roughage. The best concentrates for rabbits during this period are corn grain, barley, oats, wheat, bran, cake; from green feed - legumes, forbs; from juicy ones - carrots, beets, cabbage; coarse ones make good hay. During the main fattening period, rabbits' diets are supplemented with food that promotes maximum fat deposition - peas, barley, corn, oats, bran, cake, boiled potatoes. Root crops are completely excluded during this period. If they give you any hay, it’s not much.
In the final period, the rabbit breeder must achieve maximum feed consumption by rabbits. Rough and succulent food is completely excluded from the diet to improve the appetite of rabbits; during this period, aromatic herbs are introduced into their diets in small quantities - dill, parsley, celery, cumin, chicory, as well as 1-2 g of table salt. By the end of fattening, rabbits become inactive and completely lose their appetite. We remove such rabbits from fattening and kill them.
Types of feed
The industry produces two types of combined feeds for rabbits:
- PC – fully rationed feed. Their composition fully satisfies all the needs of the animal body for nutrients, vitamins and microelements. When using this feed there is no need for additional feeding.
- Concentrated feeds are sold under the designation K or KK. This feed supplements the basic diet of animals with protein, fiber and minerals.
Different feed options are available for different ages of animals:
- for fattening young animals aged from one to five months, PK 90, PK 91, K91 are used;
- for feeding adult rabbits use K 92-1 and K 92-2;
- For final fattening of animals for meat, K93-1 compound feed is used.
Compound feed goes on sale in two states:
- granulated. An excellent option for complete feeding. Excellent storage, easy to dose, convenient for animals to eat;
- bulk mixtures. All components in them are ground into powder. It is most convenient to use them in mash.
On a note!
Feeding feed intended for other animals or birds can be harmful to rabbits due to the specific additives included in it.
Need for vitamins
Vitamin A is essential for normal growth, development and reproduction in rabbits. A lack of this vitamin in the body leads to a decrease in its resistance to diseases. At the same time, diseases of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract develop, the fertility of females and the viability of offspring decreases. In summer, the main source of this vitamin in rabbits' diets is green food, and in winter - roughage and succulent food. Young animals receive vitamin A mainly from rabbits' milk. Green grass, carrots, cabbage leaves and grass meal are especially rich in vitamin A. In spring, the reserves of vitamin A in the body of rabbits sharply decrease, which may be the cause of A-vitaminosis. During this period, it is advisable to introduce high-quality bean hay, carrots, grass or hay flour into the diet.
Vitamin D is contained in feed in small quantities. Its active form (calciferol - vitamin D3) is already synthesized in the body of rabbits under the influence of the ultraviolet spectrum. The main function of this vitamin is to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, and its insufficient amount leads to rickets in young rabbits and osteomalacia in adults. Most often, short-haired rabbits - rexes, as well as young animals of all breeds from numerous and late litters - suffer from rickets. As a rule, when rabbits are kept in open cages, there is no need for additional feeding of this vitamin, however, with intensive rabbit breeding (indoors), vitamin D in the diet should be in quantities of 20-25 IU per 1 kg of live weight.
Vitamin E is also called the reproduction vitamin. Its insufficient amount in the diets of rabbits negatively affects spermatogenesis and the process of fertilization of females, leading to the death and resorption of embryos. Vitamin E deficiency in rabbit diets causes muscular dystrophy and myocarditis (heart disease). Experts believe that the introduction of 0.2-0.5 mg of tocopherol per 1 kg of live weight into feed eliminates the consequences of E-vitaminosis.
Vitamins C and K. Unlike other animal species, rabbits do not require significant amounts of vitamin C in their diets for normal development. Research has found that rabbits grow normally on diets that cause scurvy in guinea pigs. A lack of vitamin K in rabbit feeds can lead to abortion, but the need for it is usually met through natural content in the feed.
B vitamins are synthesized in the body of rabbits. There are quite a lot of them in the soft feces eaten by rabbits (coprophagia). A number of experiments have established that adding 0.1-0.3 mg of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3) to the basic diet increases the growth rate of young rabbits. The need for choline (vitamin B4) for them is approximately 0.13% of the dry matter of the diet. Adult rabbits without satisfying their need for choline quickly lose weight and die from liver degeneration (cirrhosis) and muscular dystrophy.
What is feed made from?
Main components included:
- grain of wheat, barley, oats, corn;
- sunflower cake;
- legume grains: beans, peas, soybeans, lupine;
- oilseed grains: sunflower, rapeseed, rapeseed;
- roughage as a source of fiber;
- bran;
- bone flour;
- mineral, vitamin supplements, biostimulants.
In addition, to improve digestion, high-quality industrially produced feed includes:
You may be interested in: Industrial cages for rabbits at home: drawings How to make drinking bowls for rabbits with your own hands Cages for rabbits with your own hands: photos, original ideas
- acetic, ascorbic, benzoic and sorbic acids;
- ammonium hydroxide as a mold inhibitor;
- beet pulp – sugar production waste;
- source of calcium – limestone or calcium carbonate;
- source of protein – rapeseed flour, made from rapeseed after pressing the oil;
- B4 or choline chloride;
- preservative – citric acid. The use of citric acid helps to enhance growth and increase immunity in animals;
- flavoring additive – corn gluten;
- magnesium oxide;
- binding component and source of magnesium – black or cane molasses;
- source of phosphorus – monosodium phosphate;
- papaya to improve digestion;
- soybean hulls as a source of fiber;
- safflower flour as a source of protein;
- rosemary extract – a perfect natural antioxidant;
- safflower oil to improve taste;
- soybean meal is a source of protein;
- yucca to normalize the animal's gastrointestinal tract.
conclusions
- Rabbits are herbivores and are voracious. An adult requires up to 10 meals per day.
- The diet of rabbits should consist of green, juicy, solid and concentrated food.
- Addition to food is necessary for animals of any age. Mineral supplements are especially important for pregnant and lactating females and young animals.
- Table salt should be present in the diet of rabbits at any time of the year.
- Feeding standards and diet differ depending on the condition of the animal, time of year, age and characteristics of the breed.
Self-production of feed
A prerequisite for this is the presence of a grain crusher. For complete mixing, all components must be ground to a homogeneous mass. To mix small volumes, you can use an electric drill with an attachment; for continuous feed production, it is easier to purchase a concrete mixer.
Full ration food recipe
- In a grain crusher, grain is ground into flour. 20% barley, 10% wheat, 10% corn, 5.5% soybeans are poured into the container.
- Add 40% of the volume of the container of chopped hay to the resulting mixture.
- Next, the sunflower cake is finely crushed and added in the amount of 10% of the volume.
- The total mass is filled with 2% feed yeast, 0.3% salt, 2.2% meat and bone meal.
The mixture is thoroughly mixed.
Determining the usefulness of purchased feed
Before purchasing feed, you must carefully study the label attached to it. The packaging must indicate what components the concentrate consists of, as well as the percentage of nutrients. In veterinary medicine, the following nutritional standards have been adopted for adult rabbits:
- raw fiber: more than 18%;
- indigestible elements: more than 12.5%;
- crude protein: 10 to 16%;
- fat: from 1 to 4%;
- calcium: from 0.6 to 1%;
- phosphorus: from 0.4 to 0.8%.
Food should contain vitamins:
- vitamin A: from 6,000 to 10,000 IU per kilogram;
- vitamin D: from 800 to 1200 IU per kilogram;
- vitamin E: from 40 to 70 mg per kilogram;
- trace elements: magnesium 0.3%, zinc 0.5%, potassium 0.6%.
Dr. Dana Krempels recommends the following ratio:
- fiber at least 22%;
- protein no more than 14%;
- fat 1%;
- calcium 1%.
On a note!
Young rabbits require food high in protein and fat.
Finding a feed composition that satisfies all the requirements is quite problematic, so when purchasing, pay attention to the most important factors. For an obese animal, the best choice would be a feed with a high amount of fiber and a reduced amount of fat, for an animal suffering from kidney problems - with a minimal amount of calcium.
Composition of ideal food for rabbits
What does the dosage of food depend on:
- from the breed
- on the color of the coat (to a lesser extent, but still)
- on the number of matings (applies to breeding rabbits)
- from the offspring brought
- from the approaching birth (for pregnant rabbits)
- from the body weight of the animal
- by age
Scientists have proven that white rabbits eat significantly less than animals of other colors. It is worth considering this when breeding white giants and the Californian breed. Smaller breeds are ready for fertilization by the fifth month, and larger ones only by the sixth. The quantity and nutritional value of food is increased for females that are covered and the litter enters the second phase.
Familiarize yourself with the calculation of feed per head in relation to the above characteristics. Remember that the figure is calculated per kilogram of the rabbit's weight.
- Young animals - 50 - 55 grams within 24 hours.
- Adult males and females - 60 - 65 grams per day. Provided that their nutrition is not limited to one industrial compound feed, but there is a distribution of succulent and roughage.
- A female waiting for offspring receives 110 - 115 grams of feed.
When choosing feed, you should take into account the physiological characteristics, age, gender, breed of the animal.
Examples of compound feed recipes with proven composition
- Feed mixture No. 1: wheat - 2 parts, barley - 3, crushed corn - 1, sunflower cake - 1, oats - 0.7, peas - 0.7.
- Feed mixture No. 2 is used for young animals: industrial feed (up to two months of age) - 1 part, barley - 3, wheat - 1, oats - 2.
- Feed mixture No. 3 is used for the growth of adult individuals: industrial feed (from two months of age) - 1 part, barley - 3, wheat - 1, oats - 2, corn - 1.
Do not forget to use green food for feeding in an amount of 30% of the daily dose and root vegetables - 5-10%. With this feeding option, your rabbits will grow quickly, produce healthy offspring and not cause problems associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and immunity.
It is worth mentioning the observance of some rules when feeding rabbits:
pay attention to the expiration dates of commercial feed; comply with storage standards; calculate the dosage and composition correctly; Keep feeders and cages clean.
The question inevitably arises about the need to buy ready-made feed or produce it yourself. For many breeders it is controversial. Therefore, we advise you to familiarize yourself with the pros and cons of compound feed prepared by yourself.
Every breeder can create a varied diet for rabbits himself.Reviews
Nikolay, 37 years old
We have a large farm, so we specially go to the feed mill to buy feed. To save money, we buy concentrates, which we add to the main diet. We directly pour the granules into the feeders, and we dilute the loose feed and give it out in mash. After switching to specialized feed, our weight gain increased and the quality of the skins improved.
Elena, 29 years old
I have a small decorative rabbit, it eats very little, I buy a full ration of food for it at the pet store. Very convenient: the bag for the animal contains a specially selected composition of vitamins, fiber, proteins, protein, and microelements. There is no need to think about what to feed your pet - just pour granules into a cup, and all problems are solved. After eating, the rabbit is always cheerful and energetic, the fur is smooth and shiny.
In modern rabbit farming, the use of compound feed is a prerequisite for obtaining stable weight gain, high-quality wool and healthy offspring.
Answers on questions
In the process of raising rabbits, some atypical problems may arise that occur in animals of any age. Let's look at some of the most common ones.
If your rabbit turns away from food
Rabbits' bodies are designed in such a way that they need to constantly chew something. This is important not only for teeth, but also for the entire digestive system. Normally, a healthy animal can have up to 10 meals per day. A rabbit may only turn away from food if there is some illness, usually an infection, viral disease or intestinal problem. In addition, this situation is often observed during teething in young animals, as well as when the rules of keeping are violated (high humidity, non-compliance with temperature conditions).
Even if a rabbit loses its appetite, it must be force-fed.
If he turns over a bowl of food
Rabbits are active animals. They often interact with other individuals and objects in the cage . They most often turn over bowls made of lightweight materials, such as plastic. To avoid this, it is recommended to purchase feeders made of ceramic or galvanized iron.
In addition, such behavior is possible due to poor quality food, as well as behavioral problems, for example, during illness or mating.
Ceramic and iron bowls are more stable and durable than plastic ones.
Often, refusal to eat occurs when there is a hairball in the intestines. A small foreign body leads to digestive problems, and if it grows, serious complications, including death, are possible.