Some people wage an irreconcilable fight with these animals, others keep them as pets.
Decorative rodent in a cup
Such a contradictory attitude towards them in humans is quite understandable, since we are talking about rats.
Both will be interested in how many years rats live: domestic and wild rodents. The lifespan of these animals directly depends on the conditions under which it occurs.
To what age do they grow?
Rats grow and develop quickly. This process occurs most actively from birth to 6 months:
- On days 3–4, the ears open.
- Teething begins on days 9–10.
- Eyes open after 2 weeks.
- By day 16, the fur already completely covers the body.
- Molars erupt in 35–40 days.
- At 3 weeks of age, puppies are already eating from the feeder.
- On the 25th day, the babies are separated from their mother.
In addition, the growth of puppies does not stop, but becomes less noticeable. At the age of one year, animals become fully formed. During this period, their weight is 300–600 g: females grow twice as large as males.
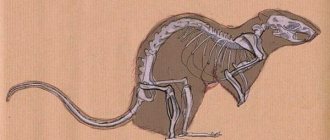
Rodent anatomy
The animals have a stocky build and an oval body shape. The size of an adult individual can be 8–30 cm in length. Body weight is 37–420 g. Some individuals weigh more than 500 g.
Many people wonder how many fingers rats have. The animals' front paws resemble human hands, but each has 4 fingers. The fifth (large) has a reduced shape, looks like a short stump with a blunt end. There are 5 toes on the hind legs.
How many teeth do rats have? There are a total of 4 incisors and 12 molars. The former are constantly growing, so animals have to regularly grind them down on various objects and materials.
If the rodent does not do this, the incisors will soon grow, preventing the mouth from closing normally. This causes severe discomfort, so when keeping pets at home, it is necessary to give wooden blocks and branches to your pets. Then the animal will be healthy and calm.
The structure of the rat has its own distinctive features:
- normal body temperature: +37.5ºС - +38.3ºС;
- heart rate per minute: 300 – 500;
- number of breaths per minute: 85 – 100;
- with a weight of 400 g, the animal’s brain is 2 g;
- puberty occurs after 8 weeks of age;
- pregnancy lasts up to 24 days.
Physiology is designed so that rats can survive in a variety of conditions:
- eyes. They allow you to see well around you, but not those objects that are very close. Animals have difficulty viewing stationary objects.
- Ears. Rodents have excellent hearing. The ears can move in different directions, independently of each other.
- Nose. Compared to humans, rats perceive a wider range of aromas. This allows her to identify strangers by smell and recognize the marks of other animals.
- Taste buds. They detect the quality of food even if there is a subtle aftertaste.
- Vibrissae. Helps with orientation in the dark.
The animals have a well-developed sense of heights, so they can calmly rest even on tight ropes.
What factors does it depend on?
Experienced breeders know how long rats will live at home - this largely depends on the pedigree of the animals. In other words, the lifespan of a house mouse is directly related to genetics.
If parents are sick, they will not have healthy children. Weak children are also born from close relatives. These children live short lives and often get sick. Only healthy animals with the desired coat pattern and color are selected for crossing.
Accordingly, in order for pet rats to please their owners for a long time, it is advisable to purchase them in kindergartens, where specialists monitor the reproduction and treatment of their charges.
In addition to the child’s pedigree, future nursery owners will be told how to care for them, what they can and should be fed, what vaccinations they received and what needs to be done.
A healthy and rich diet for your pet will also ensure a long and happy life. Human food and junk food can cause illness and premature death in an animal.
Do not spoil your pet with chips, sweets and other similar treats.
The living conditions of pets are very important, so it is necessary to provide rats with everything they need.
What can you feed and what can you not?
Balanced feeding of the right foods will prolong the life of the animal and avoid many diseases. Animals of this species are considered unpretentious in nutrition, but the following list of foods is prohibited for them:
- any sweets, especially chocolate and candies;
- sweet drinks and sparkling water;
- raw beans and legumes;
- Brussels sprouts and red cabbage;
- raw potatoes;
- smoked sausage;
- fried meat seasoned with spicy seasonings;
- alcoholic drinks;
- spinach;
- unripe bananas;
- shashlik;
- chips and similar snacks.
Shish kebab The
diet of a domestic rat must include the following food products, which will provide it with a healthy, balanced menu:
- Sunflower, flax and pumpkin seeds, oat sprouts and greens, millet and wheat, which serve as vitamin supplements.
- Dry cereal mixtures in crushed form, they may include: barley, rice, corn and wheat. Such food is the basis of the diet of a decorative rat.
- Almost all vegetables are allowed, except those listed on the list of prohibited foods. It is recommended to give vegetables regularly for normal intestinal motility and saturation of the animal’s body with useful vitamins and substances.
- Dried fruits and berries - as a treat.
- Fermented milk products, which are a source of calcium for rats. These include: kefir, fermented baked milk, unsweetened yogurt and low-fat cottage cheese.
- Protein food should also be present in the rat's diet in the form of boiled eggs, chicken, fish and cooked meat by-products.
In addition to the main products that make up a rat’s daily diet, you should not lose sight of the opportunity to occasionally treat the rodent with pieces of apple or watermelon, puffed rice or corn.
It is important not to mix different types of food in one feeding.
How to extend the life of a pet?
The lifespan of a decorative rat largely depends on nutrition. The following expert tips will help you create the right diet for your pet:
- It is unacceptable to feed rats in large portions - this can lead to obesity and rapid death of the animal.
- Food for pet mice should be rich in antioxidants: the presence of free radicals in the body contributes to the development of diseases and accelerates the aging process.
- When purchasing food, you should only choose food that is specifically made for mice.
Another important factor is care and attention. Rats do not like high temperatures or cold, so it is necessary to install a house for them in a warm, dry room, without drafts, but away from radiators or heating devices. The house itself should be large enough to allow its occupant enough space to move around.
If the TV is often on in the room or people listen to music, it is better to move the rat house to another warm but quiet room. Rats do not like the frequent presence of strangers or animals.
Communication is no less important for mice: in nature, rodents live in groups, so they have difficulty withstanding loneliness. It is better to buy not just one pet, but two or three, so that they can communicate not only with people, but also with their fellow creatures.
Impact on the life expectancy of a home
The lifespan of rodents is greatly influenced by the arrangement of the cage. If the cage is small and does not contain entertainment structures, the pet will be inactive. This will negatively affect your well-being in the future. This may cause:
- the occurrence of excessive body weight;
- muscle atrophy;
- cardiovascular pathologies.
The cage should not be placed in direct sunlight. The animal may overheat. Decorative rats do not tolerate heat well. It can cause a cold. The dwelling is located in the shade, but not placed in a dark place. You cannot use an aquarium instead of a cage. There is not enough air entering the vessel. All food and water containers must be kept clean. It is important to change the filler as often as possible.
How long do rats live at home?
The lifespan of a house mouse can exceed 2.5 or even 3 years. Very rarely, animals of this species live up to 4 years. It is interesting to note that with the same care and maintenance, the average life expectancy of males is longer than that of females.
A record of a long-lived rat that lived for 7 years and 3 months was entered into the World Book of Records. But these centenarians are the exception to the rule. In fact, a two-year-old mouse is no longer a lady of “Balzac age,” which is noticeable in its appearance, state of health and activity. At 3 years old, a house mouse is considered a decrepit old woman.
Wild mice in nature and near humans
These small rodents are widespread throughout the globe. Endurance, the genetically inherent ability to quickly adapt and survive in difficult conditions, and unpretentiousness in nutrition allow mice to survive even in the Far North, high-mountain and arid regions.
House mice
All wild mice can be divided into 2 large groups:
- those that settle directly in forests, fields, haystacks, tree hollows, and rodents;
- those who live next to a person, but independently.
The latter try not to catch the eye of people; in fact, they are wild. But in terms of nutrition, such mice have a much easier life than their wild counterparts. They use the reserves accumulated by people and spoil food and grain. For this, animals often have to pay with their lives: they get caught in mousetraps, are poisoned by pesticides, and die in the paws of domestic cats.
The weight of a house mouse is 12–35 g. The body of the rodent does not exceed 10 cm in length, the tail is much shorter than the body (its length is approximately 4–5 cm). If a house mouse is hungry, it can feed itself not only with food, but also, for example, with candles or soap. The animals are very fertile, producing 4–10 litters of mice annually. Each litter of house rodents contains at least 3 cubs, most often 10–12 animals, which mature within 1.5 months.
Such mice do not have to live in poverty without food . Their main problem is to avoid traps and domestic predators. It's no surprise that rising house mouse populations are a major threat to agricultural supplies. Farmers go to great lengths to get rid of unwanted neighbors. Despite this, house mice live longer than their wild counterparts by 2–3 years thanks to food reserves and constant access to water.
Natural rodents
A distinctive feature of all mice is their gluttony. The availability of food in the habitat of wild rodents becomes a determining factor of survival for animals.
Table 1. Features of the most famous mouse species
| Name | Approximate body length (cm) | Peculiarities | Habitat |
| Shrew | 7–10 | Elongated muzzle shape | America, Australia |
| Lesnaya | 10–12 | The fur is grayish-brown, light on the belly. Red spot on chest | Siberia, Altai, Ukraine, Belarus |
| Field | 8–13 | Elongated muzzle, pointed ears. The fur is golden brown, with a dark stripe along the back. | Lowland areas of Europe, Asia |
| Gerbil | 15–20 | Reddish-gray or ocher color. There is a fluffy tassel on the tail | African deserts, Asia, Eastern European steppes |
| Herbal | 25–30 | Settle near bodies of water | South Africa |
| White | 8–11 | The fur is white. The first domesticated mouse species | Northern latitudes, high mountain regions |
The food supply conditions for mice living in the wild are constantly changing. They depend on many reasons:
- weather fluctuations;
- crop yields in nearby fields;
- human intervention;
- changes in the composition and number of competitors and predators.
Mice have an accelerated metabolism. These animals are forced to eat 5 times a day to maintain their strength. For 1 adult, 3–5 ml of water per day is enough. If a mouse lacks fluid, it makes up for it with juices from plants (in summer) or melted snow (in winter).
Interesting! Mice's innate ability to adapt, coupled with incredibly high fertility, helps them survive and maintain their population in nature.
Scientists have proven that the life cycle of wild rodents does not exceed 4 years. But in fact, the average lifespan of a mouse in its natural environment is about a year. The rare animal survives in the wild for up to one and a half years. The reason that wild mice do not live long is the harsh, dangerous conditions of the surrounding world.
The lifespan of mice is affected by:
- presence or absence of food;
- excess moisture;
- drought - mice have a hard time with a lack of water; it is much easier for them to endure a lack of food than to suffer from thirst;
- the presence of sown fields with irrigation systems in the territory where rodents live - this helps mice survive and increases the duration of their life cycle.
Interesting! It is mice, with their accelerated metabolism, that are regularly used for experiments to increase life expectancy.
How do the life spans of different breeds of rats differ?
The lifespan of rats is 1.5–3 years. A more accurate indicator depends on the breed:
- Sphinxes. Hairless rats are much weaker than their furry counterparts. This is due to the lack of not only hair, but also the thymus gland, which is responsible for the production of immunity. Hairless pet rats live for about 6–12 months.
- Albinos. White rats live as long as their relatives of other colors: the life expectancy of rodents does not depend on the color of their fur. If the mouse was purchased from a reputable breeder and was properly cared for, the animal can live for about 3 years.
- Dumbo. Animals of this breed live much longer than their hairless relatives, but almost as long as albinos - about 3 years.
The indicated life expectancy of rats of all breeds is possible provided that their parents were not close relatives.
Peculiarities
The domestication of tailed animals began at the beginning of the last century. Decorative rats have a keen intelligence, have excellent memory and are highly trainable. In this regard, the popularity of rodents as pets is increasing every year. Even those who do not have warm feelings for rats watch with interest the antics of the eared animals.
The domestic rat is a compact pet. Adults weigh from 300 to 600 grams depending on gender. Boys grow up to be almost twice as big as girls. Most breeds have a slightly elongated muzzle, ears set high and with rounded tips. The body is covered with fur, its thickness and length depends on the specific breed. The tail is most often bare or covered with a small amount of hair. It is noteworthy that in some individuals it is warm to the touch, while in others it is cold.
What you need to know to properly keep rats at home.
How to determine the age of a rat?
People usually project the age of animals as human. To calculate the age of rats by human standards, the number of months they have lived must be multiplied by 2.5, and the resulting figure should be counted as years. Thus, animals aged 6 months are approximately 15–16 years old by human standards. A one-year-old animal is 30 “persons”, a two-year-old animal is 60, and so on
Veterinarians and experienced breeders are well aware of how to visualize the age of a mouse. First of all, this is weight:
- Two-day-old animals weigh about 150–220 g.
- After a day, their weight increases to 210–310 g.
- Four-day-old females weigh about 230 g, and males weigh about 280 g.
- At 5 days of age, males weigh 450–500 g, and females weigh 280–300 g.
Elderly people are different:
- Fat distribution: Old men have no fat on their backs, so their spine is clearly visible.
- Appearance of fur: in young rats it is shiny and thick.
- By the size of the incisors: the longer they are, the older the animal.
- Due to the appearance of the tail, the skin on it in middle-aged rats becomes rougher and rougher, and begins to flake off.
- Along the length of the tail. After 6 months, the rats' tail begins to actively grow - previously it was shorter than the body.
Kinds
The mouse subfamily includes about three hundred species, each of which is characterized by external and behavioral features.
Despite significant differences, most species have a number of similar characteristics. Types of mice, typical features, and brief characteristics of the species are given below.
African mice
Unlike most of their relatives, African mice, whose homeland is called Tunisia, are not synanthropic species and are practically not tamed.
The body length of such a mouse is no more than twelve centimeters. The color is interesting: light brown or sandy fur has several dark longitudinal stripes. Rodents do not have a pleasant odor, which sets them apart from representatives of most other species.
The typical habitat of African rodents are burrows dug in the sand or nests made in dry grass. Their food is cereals, fruits, insects, and larvae.
The natural lifespan is about four years, but in the wild rodents can live no more than a year, due to the large number of natural enemies.
Grass mice
Grass mice live on the African continent. The body size of representatives of this species ranges from ten to seventeen centimeters.
Rodents prefer to settle in humid environments, for example, along the banks of rivers and lakes. Grass mice can build houses on their own, using dry grass, fluff, and also occupy other people's homes.
Lesnaya
A distinctive feature of wood mice is a small spot on the chest that has a yellowish tint.
These rodents are common in areas with temperate climates. Rotten stumps, dry grass, tree roots, and other voids of natural origin can serve as housing for them. Wood mice feed on cereals, insects, and berries.
Yellow-throated mouse
The yellow-necked mouse is classified as a poorly studied species listed in the Red Book.
The decline in the population of this species is due to the specific habitat; these tiny rodents, whose body length is no more than ten centimeters, live exclusively in deciduous forests.
Gerbil
The gerbil mouse fully lives up to its name, as it lives in hot deserts, semi-deserts, and steppes.
This breed of mice is distinguished by the presence of a long fluffy tail, which tends to fall off when in danger. A new one does not grow back. The diet of gerbils consists of cereals, insects, seeds, fruits, and nuts.
Gerbils can jump long distances and move on their hind legs. These rodents lead an active lifestyle during the daytime. In winter they do not hibernate, but become lethargic and inactive.
Gerbils are light brown in color, with the fur on their bellies being several shades lighter.
Harvest mouse
The field mouse lives in areas with temperate climatic conditions. The shades of the rodent's fur can vary from light brown to black; there is a longitudinal contrasting stripe on the back.
The body size of the animal is no more than ten centimeters. Mice of this species can live in urban areas. Their food sources are cereals, invertebrates, insects, fruits, and nuts.
House mouse
House mice are called synanthropic species of rodents that live close to human habitation, feed on food supplies, and prefer to spend the winter in houses and apartments.
The size of the rodent varies from eight to five centimeters. They are unpretentious to external conditions and nutrition. Life expectancy is about two years, but in good conditions the rodent can live up to four years.
Shrew
The shrew is a type of mouse that digs and also has a long, thin nose. The coat color of these animals is uniform and can vary from gray to black.
Shrews feel especially good near natural bodies of water.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any pet, an ornamental pet has a number of advantages and disadvantages. The positive aspects include the following:
- receptivity to training;
- high intellectual level;
- unpretentiousness in food;
- response to nickname;
- presence of a good-natured and affectionate character;
- sociability;
- gullibility;
- no need for spacious living quarters;
- cleanliness;
- creating a minimum amount of noise;
- low maintenance costs;
- ease of care.
The animal has the unique ability to adapt to the mood of its owner, giving the person exactly the emotions that he needs. The main disadvantages of a funny animal are:
- failure to follow commands without a treat;
- falling into depression after being alone for a long time;
- incompatibility with predatory domestic animals;
- territory label;
- damage to all available interior items;
- high cost of medications for treatment;
- presence of a specific odor;
- need for daily walk;
- high price;
- short period of life;
- maintaining wildness in the absence of contact with people.