- home
- General information
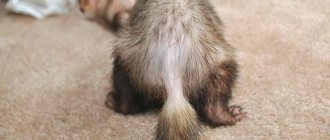
11/04/2018 Coprostasis, or constipation in a hamster, is a digestive failure, expressed in difficulty in defecation or regular incomplete bowel movements. This is an extremely dangerous condition for little furbabies. It causes intoxication, the appearance of fecal plugs, intestinal prolapse and can result in the death of the animal. Therefore, coprostasis requires urgent treatment.
What to do if your hamster is constipated
Every day the charming hamster cheers up its owner and goes into his arms.
Suddenly, the affectionate rodent becomes extremely restless and its abdomen swells. What should an owner do if a hamster is constipated? It is necessary to help the animal cleanse its intestines; constipation can cause poisoning of the body, the formation of coprostasis, rectal prolapse from the anus and death. It is usually the owner's fault that a hamster does not poop. If a rodent does not have access to drinking water and eats a lot of dry food, then it gradually develops constipation. Fiber is a biological causative agent of peristalsis; it is found in buckwheat, couscous, oatmeal, corn, fruits and vegetables. An unbalanced diet is the main cause of this unpleasant disease. Sometimes a hamster does not have bowel movements due to anxiety, various diseases of the small and large intestines, and mechanical damage.
LACTOSTASIS OR MASTITIS - WHAT TO DO AND HOW TO AVOID?
Painful lump in the breast, redness, temperature - these words frighten almost every expectant mother. And it is with these complaints that nursing mothers very often turn to specialists. The diagnosis they hear is “lactostasis” or “mastitis”. These two diagnoses are often confused and even considered synonymous. Confusion also exists in specialized literature, and even more so in the stories of nursing and breastfeeding women.
Lactostasis is stagnation of milk caused by blockage of the duct. Milk accumulates, does not come out, and bursts the “locked” lobule, causing pain. Reabsorption of milk can provoke a rise in temperature. The filled lobule compresses the surrounding tissues, this causes swelling, which further complicates the release of milk.
Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue . Characteristic signs of inflammation are pain, redness and temperature, although often the picture can be blurry, for example, a slight temperature. Mastitis in a nursing mother is most often the result of prolonged lactostasis (swollen, injured tissues easily become inflamed), but it can also occur without previous stagnation, due to infection (for example, through cracks in the nipple or from foci of infection inside the body, as a consequence of an acute or chronic disease).
Understanding what exactly is happening to the breasts is not as easy as it seems. This is difficult to do by eye. Lactostasis can occur with severe pain and high fever, while mastitis can occur without fever. It is not always possible to palpate a lump, especially a deep one, and a specialist cannot always differentiate for sure what kind of lump it is - a lobule full of milk, or edematous tissue, or an abscess. Ultrasound comes to the rescue today, so if you have the slightest doubt, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound examination. Moreover, in addition to its diagnostic role, it can also help therapeutically - ultrasound often “breaks” the plug and helps cope with lactostasis.
What to do?
But the nursing mother herself is usually not interested in the complexities of diagnosis. What is more important to her is what to do in a particular situation. Does it really matter what exactly happened? Yes. Because the treatment tactics are different. And if lactostasis can most often be dealt with on your own in a day or two, then mastitis usually requires the help of a specialist and often the use of antibiotics.
So, the first day after the onset of symptoms (pain, redness, thickening, rise in temperature) most often suggests lactostasis . You can try to cope with it with the following measures:
- The first and most important thing is to empty the sore breast well.
People often think that this requires a super-master of pumping or a mega-cool breast pump. However, the best assistant in emptying the breast is a properly sucking baby. Therefore, our first remedy will be frequent feeding from the sore breast.
If the baby sucks ineffectively (incorrectly attached to the breast, weak), rarely (for example, a child of the second half of the year or older than a year may breastfeed quite rarely), additional pumping may be useful. If there is a lot of milk and the baby's sucking is not enough to solve the situation, it is better to express the milk before feeding, and leave the baby the difficult job of sucking the milk out of the problematic ducts.
- Warmth before feeding/pumping (warm shower, warm diaper on the chest) may help;
- Cold after feeding/pumping has worked well (a bag of frozen berries wrapped in a diaper, a cloth soaked in cold water);
- You can massage the lump, but carefully - a hard massage increases the swelling and worsens the situation;
- drink when thirsty, it is better to drink plain cool water (hot drinks can increase the flow of milk) Limiting drinking will not help, on the contrary, if dehydrated, the milk may become thick, and it will begin to leak out even worse;
- If there is no improvement within 24 hours, you should seek help.
What should not be done if milk stagnation occurs?
- You can't stop feeding
- It may be risky to make vodka, alcohol, camphor compresses (may worsen milk secretion, there may be burns to the skin of the breast)
- There is no need to resort to hard, traumatic “kneading” of the chest - this can lead to injury and worsening the situation.
- Don't expect spontaneous improvement. If no progress is visible within a day or two, especially if it gets worse, you need to seek help.
Who should I turn to for help ?
- In case of mastitis, a woman needs to see a doctor , mammologist or gynecologist to make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed that are compatible with breastfeeding (that is, the active substance either does not penetrate into milk or penetrates in such small doses that it has no effect on the child).
- Be sure to continue feeding from the affected breast. An exception is made in the case of purulent mastitis - during the period of discharge of pus from the ducts, it is necessary to stop feeding the affected breast and express milk; after the end of the discharge of pus, feeding resumes. With healthy breasts, feeding is not interrupted.
Minimize risk
Expectant mothers are very concerned about how this situation can be prevented. There are no guaranteed methods. It happens that despite all efforts, stagnation of milk still occurs. But you can try to minimize the risks.
- Put your baby to your breast frequently (in the first month, breaks of more than 2 hours are undesirable).
- Make sure your baby is properly attached to the breast. An incorrectly sucked baby will empty it. If you are unable to put your baby to your breast, if congestion appears in the first month, it makes sense to seek help from a lactation consultant.
- Try to drink enough water.
- Avoid chest compression (tight underwear, underwired bra, pressure from the shoulder strap of a bag, backpack or baby carrier, sleeping on your stomach can lead to congestion).
- Do not let your baby suck on anything other than the breast (sucking on nipples and pacifiers increases the risk of lactostasis).
Let all these tips remain just “general information” information and feeding will be easy and problem-free. But even at the first signs of problems, there is no need to panic - with competent actions and timely seeking qualified help, most difficulties are quickly resolved.
Health to all nursing mothers and their wonderful babies!
Anastasia Vtulova, consultant on breastfeeding and child care (Center for Natural Development and Child Health)
You can consult our breastfeeding hotline:
+7 (daily from 7.00 to 23.00).
Previous
Next
Causes of constipation in a hamster
Typically, intestinal dysfunction in hamsters develops due to the fault of the owners. The reason is insufficient intake of moisture and fiber. Thus, constipation is primarily caused by excessive consumption of dry food and insufficient drinking water. Fiber starts the digestion process. It is found in vegetables, fruits and grains. The lack of such food in the animal’s menu is the root cause of the development of the disease. Less common factors are stress, trauma and intestinal pathologies.
Causes of the disease
A large group of inflammatory processes in the conjunctiva, which have significant differences in causes, epidemiology, dynamics, prognosis, etc., is collectively called “conjunctivitis.” In ophthalmological practice, various classifications of conjunctivitis are used, but, as a rule, they emphasize the etiopathogenetic factor, i.e. causes and mechanisms of inflammation, for example:
- infectious conjunctivitis:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- dystrophic conjunctivitis;
- chronic conjunctivitis (usually caused by prolonged mechanical, ultraviolet or chemical irritation, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine disorders, inadequate treatment or self-medication);
- parasitic conjunctivitis, etc.
The first two types are the most common; In general, conjunctivitis is considered the most common diagnosis in ophthalmology, and especially in children's.
Treating constipation in a hamster at home
What to do if it becomes clear that your hamster is constipated? First of all, it is necessary to provide it with water and a small amount of succulent food, vegetables and fruits. It is better not to give hamsters laxatives. Instead, the animal is given 1–2 ml of Vaseline oil from a syringe. You need to carry out two such procedures with a difference of 20 minutes, then wait 4 hours. If the intestines have not emptied, the hamster continues to be fed with oil.
To alleviate the condition, you can inject a little vegetable oil or a mixture of baxopan with paraffin oil into the anus. This must be done very carefully so as not to damage the thin mucous membrane. Therefore, it is better to have this procedure performed by a veterinarian. After this, it would be useful to massage your pet’s tummy clockwise, and then make him move, run, and play. This activates the digestive processes.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in a child
The main complaints, common to all ages and types of conjunctivitis, include redness and characteristic clouding of the eyes, noticeable redness of the edges of the eyelids, increased flow of tears (in some cases with mucopurulent exudate), burning, stinging, itching, foreign body sensation and other symptoms. Depending on the damaging factor and the type of course, the severity of symptoms varies from quite tolerable to painful. In terms of age, however, it should be noted that for the youngest patients there are simply no “tolerable” symptoms; in other words, at the first signs of inflammation of the conjunctiva, measures should be timely and, most importantly, adequate.
Considering that conjunctivitis is not at all as harmless as it often seems to adults, and in some cases is fraught with dangerous complications, the most adequate reaction of parents is to contact an ophthalmologist, the least - an attempt at amateur drug therapy for childhood conjunctivitis.
Treatment of constipation in a hamster in a veterinary clinic
If your hamster's stool does not return to normal within 24 hours after starting treatment, you need to go to the veterinarian. The doctor performs an ultrasound and prescribes treatment. To cleanse the animal's intestines, he gives an enema using painkillers. In case of intoxication and dehydration, the doctor injects the hamster subcutaneously with Ringer-Locke solution. To normalize the intestinal microflora, the veterinarian recommends a special probiotic. After a few days of examination, the hamster should recover. But if intestinal obstruction occurs, surgical intervention and rehabilitation are necessary.
After treatment, the animal is fed for some time with semi-liquid plant food: boiled buckwheat, carrots, prunes, oat leaves, parsley, dill. You can add some sunflower seeds. Dairy products, meat, eggs, flour products and dry food should not be given.
Our services for examination, prevention and treatment of hamster diseases
| A visit from a veterinarian to your home | 500 rub. |
| Examination, diagnosis, prescription of treatment for a hamster | 1000 rub. |
| Cleaning the cheek pouches | 800 rub. |
| Hamster vaccination | 1000 rub. |
| Therapy for a hamster | From 200 rub. |
| Surgery for a hamster | From 3000 rub. |
A complete list of services provided by the specialists of the veterinary service Paw of Help for Your Pets>>
Clinical signs of toxic hepatitis
Signs of an acute form of the disease
Symptoms of toxic hepatitis are very variable and in most cases depend on the degree of poisoning and on which particular toxic substance provoked the development of the pathological process.
However, there are also characteristic signs that are common to all types of toxic hepatitis:
- fast fatiguability;
- loss of appetite;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching;
- bloating;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowing of the sclera, skin and mucous membranes;
- increase in body temperature to 37–38 °C.
Many patients with toxic hepatitis develop a rash on the skin, accompanied by itching of varying intensity, urine becomes the color of dark beer, and stool becomes light-colored with a clay consistency. Often, liver damage is accompanied by an increase in the size of the organ, the appearance of small hemorrhages on the skin, bleeding gums and nosebleeds (a consequence of the destructive effect of toxic substances on the walls of blood vessels). In some cases, lethargy or excessive agitation, hand tremors, and spatial disorientation are observed.
Signs of a chronic form of the disease
As the disease becomes chronic, the symptoms of toxic liver damage become less pronounced. Typically, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- periodic pain in the right hypochondrium, worsening after eating;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- decreased performance;
- fatigue;
- flatulence;
- nausea;
- occasional bouts of vomiting;
- stool disorders;
- hepatosplenomegaly (marked enlargement of the liver and spleen).
During remission, symptoms may subside, but during an exacerbation they reappear.
Types of constipation
It is very important to classify acute and chronic constipation. In the first case, we are talking about sudden constipation - against the background of general health or exacerbation/acquisition of other diseases. Chronic constipation is diagnosed when symptoms persist for 3–6 months. The main criteria for determining constipation include the following:
- the need to strain at least in 25% of cases of defecation;
- dense, fragmented, dry feces;
- the need for manual assistance during defecation, etc.
Based on their origin, constipation is divided into many types.
Psychogenic
This type of constipation is quite easy to identify for the person himself. It occurs against the background of mental disorders and diseases: anorexia nervosa, depression, neuroses and phobias, etc. It is worth noting that constipation can also be called psychogenic when a person consciously restrains the urge to defecate, for example, avoids going to the toilet at work. False shame can lead to serious problems.
Neurogenic
This type of constipation is caused by dysregulation of intestinal motility. The condition can accompany tumors of the spinal cord and brain, previous injuries and strokes, Alzheimer's disease, etc.
Dyskinetic
Associated with intestinal dyskinesia. Muscle tone disorders can be independent and occur as a result of inflammatory diseases, pathologies of the genitourinary system, etc.
Spastic
It is a consequence of spasms of intestinal smooth muscles. It can develop against the background of stress, emotional stress and other factors.
Nutritional
This type of constipation is associated with an unbalanced diet, consumption of constipating foods, and poor drinking. Usually we are talking about a diet that is dominated by sweets, confectionery, bread, and pasta. Lack of dietary fiber leads to functional disorders. Normalizing intestinal function in this case is quite a simple matter: just review your diet and drink enough liquid.
Hypodynamic
Difficulties in defecation can occur in people who are forced to remain in bed, have a sedentary job, or lead a sedentary lifestyle. Older people are more likely to suffer from constipation.
Proctogenic
This type of constipation is associated with diseases of the rectum and anal area. The most common obstacles to normal bowel movements are anal fissures, fistulas, hemorrhoids, inflammatory diseases - proctitis, paraproctitis. In this case, constipation may be accompanied by mucous, purulent, and bloody discharge.
Mechanical
Stool retention occurs due to the fact that the movement of feces is hampered by tumors, narrowing of the lumen, and enlargement of nearby organs. This may be due to intestinal polyposis, adhesions, neoplasms and other diseases.
Endocrine
Such constipation is associated with changes in hormone levels as a result of endocrine diseases, menopause, pregnancy, and the postpartum period.
Medication
Constipation can be caused by taking medications. Painkillers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, hormonal drugs, antibiotics, diuretics and other drugs may have this effect. The condition may resolve after stopping the medications, so you should consult your doctor about a possible treatment alternative.
There are other types of constipation - associated with intoxication, dehydration, systemic diseases, etc. Serious causes of constipation are quite rare. Usually this disorder is functional in nature. Thus, researchers Marinchuk A. T., Bogatyrev V. G. and others in their scientific work claim that “constipation in 80-90% of cases is of a functional nature, the rest is caused by reasons of an organic nature” (Marinchuk, Bogatyrev, Babieva, Kumbathiadis , 2012, p. 53). However, despite this, eliminating only one cause will not be enough. To normalize intestinal function, it is necessary to adjust your lifestyle, nutrition, drinking regimen, and daily routine.
Anatomy of the colon
The colon consists of the following sections: cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon. The cecum has the widest lumen, and the sigmoid colon has the smallest. The junction of the sigmoid colon and the rectum is designated as the rectosigmoid junction. It is important to note that this section of the intestine has the narrowest diameter.
The wall of the colon consists of three layers: serous, muscular and mucous. The function of the mucous membrane of the colon is the absorption of water, the formation of feces, preparing them for evacuation by secreting a large amount of mucus and the synthesis of vitamins B and K. Under the epithelium of the colon mucosa there is a submucosa, represented by loose fibrous connective tissue in which blood vessels and lymphatic vessels and submucosal nerve plexus.
The muscular layer has a frame function and is responsible for the progressive movement of feces to the rectum. The muscular layer consists of a continuous inner circular layer, divided into three ribbons of the outer longitudinal layer.
The serous membrane consists of a connective tissue base covered with mesothelium, into which outgrowths of adipose tissue, the so-called fat pads, penetrate from the muscular layer.
What is intestinal diverticulum?
Diverticula are pouch-shaped protrusions of the intestinal wall that form in “weak” areas of the intestinal wall. There are true diverticula, which have all layers of the intestinal wall in their structure, and false ones, in which there is no muscle layer.
The diverticulum is divided into the mouth, the neck, the body and the bottom of the diverticulum. The blood supply to the diverticulum is carried out from the vessels of the submucosal layer from which thin vascular branches extend, piercing the intestinal wall and heading to the bottom of the diverticulum.
When a diverticulum forms in the projection of the fatty suspension and mesentery of the colon, it is covered on the outside with adipose tissue; when a diverticulum forms in the free edge of the intestinal wall, it is covered on the outside only with a serous membrane.
Based on the number, a single diverticulum and multiple diverticula of the colon are distinguished.
Based on the location of diverticula, right-sided, left-sided and total damage to the colon is distinguished.
Diverticulosis of right-sided localization, as a rule, is congenital in nature with a predominance of true diverticula.
With left-sided localization, diverticulosis is in most cases acquired and there is no muscle layer in the structure of diverticula.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of toxic hepatitis includes instrumental and laboratory methods that are also used in identifying other acute and chronic liver lesions. During the first medical consultation, a physical examination and history taking are performed. In most cases, this allows you to get a rough idea of the reasons that triggered the development of toxic hepatitis.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing liver damage:
- biochemical blood test - determination of the level of direct, indirect and total bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, AlT and AST and γ-GTP;
- coagulogram - prescribed to assess the state of the hemostatic system;
- general blood and urine tests;
- tests to exclude the presence of other forms of hepatitis.
Instrumental diagnostic techniques:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- liver scintigraphy;
- MRI;
- laparoscopic examination with targeted puncture biopsy of the liver.
Epidemiology
Applicable to Russia and the former USSR, one can note the rapid increase in the incidence of diverticular disease. In 1970, the incidence of the disease did not exceed 2-3 per 100 thousand population. In 1979, this number increased almost 6 times. According to data published by the State Research Center in 2002, the number of diverticulosis detected during X-ray examination was 14.2% of all coloproctological patients, and already in 2012 this figure doubled and amounted to 28.8%.
The growth of this disease is clearly visible along with the process of industrialization and urbanization due to changes in people’s way of life, lifestyle and nutrition. A decrease in the amount of dietary fiber consumed, a large amount of carbohydrate foods and consumption of red meat led to a significant jump in cases of diverticulosis.
In contrast, in developing agricultural countries, diverticular disease is characterized by isolated cases, which is determined by the nature of the diet, which includes a significant amount of plant foods.
The aging of society is another reason for the increase in the incidence of diverticular disease. It is noted that under the age of 40 years, the risk of developing diverticulosis varies between 5-10%. Whereas at the age of 60 years, the percentage of detected cases of the disease is already 30%, and by the age of 80 it exceeds 66%.
Thus, diverticular disease was, is and remains a serious problem posing difficult challenges for doctors and patients.
To understand the term diverticular disease, a brief description of the anatomy of the colon is necessary.
Planned surgical treatment of diverticulosis
As a rule, after a single attack of diverticulitis, surgical treatment is not indicated, but may be recommended for persons under 45 years of age. The decision to perform an operation is made individually.
After successful conservative treatment of two or more episodes of diverticulitis, elective surgery is recommended. The indications for elective surgery are limited by the high anesthetic and surgical risks identified during examination of the patient.
Elective surgical treatment is mandatory after conservative treatment of complicated diverticulitis.
Planned surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of fistulas.